Methane Molecule OU News
Methane (CH4) is a colorless, odorless, and highly flammable gas composed of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. It can be produced naturally and synthetically, and when burned in the.
Carbon Biology I

The tetrahedral structure of methane (CH4) is explained in the VSEPR (valence-shell-electron-pair repulsion) theory of molecular shape by supposing that the four pairs of bonding electrons (represented by the gray clouds) adopt positions that minimize their mutual repulsion. (more) Methane is lighter than air, having a specific gravity of 0.554.
Model Of A Methane Molecule Methane Png Clipart (631816) PinClipart

It consists of four hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom and is the simplest alkane. When natural methane reaches the surface of the atmosphere is called atmospheric methane and can be found under the seafloor as well as below the ground. It is odourless or has a sweet oil type smell and has no colour. It is a flammable non-toxic gas.
Methane Natural Gas Molecule Photograph by Molekuul Pixels
The Lewis structure of the methane (CH4) molecule is drawn with four single shared covalent bonds between the carbon and hydrogen atoms each. Moreover, as there exist sigma bonds only and one 2s and three 2p orbitals of the carbon produce four new hybrid orbitals, the hybridization of CH4 is sp3. It is interesting to realize that irrespective.
Pin on Χημεία

Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon, consisting of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas. Shown here are four representations chemists use for methane. In the colored models, carbon is light gray and hydrogen is white. UCAR Methane is flammable, and is used as a fuel worldwide.
3d methane molecule

Even though they are composed of only two types of atoms, there is a wide variety of hydrocarbons because they may consist of varying lengths of chains, branched chains, and rings of carbon atoms, or combinations of these structures. In addition, hydrocarbons may differ in the types of carbon-carbon bonds present in their molecules.
Methane molecule. Atoms are represented as spheres and are colourcoded

Bonding in Methane. Each C-H bond in methane, then, can be described as an overlap between a half-filled 1 s orbital in four hydrogen atoms and the larger lobe of one of the four half-filled sp3 hybrid orbitals form a four equivalent sigma (σ) bond. This orbital overlap is often described using the notation: sp3 (C)-1 s (H).
Explain how the models you developed show that when methane combines

combustion of methane and oxygen as a model of a similar reaction. Students will use atom model cut-outs to model the reaction and see that all the atoms in the reactants. Show students that the atoms in methane and oxygen need to come apart like in their models. Also point out that the atoms arrange themselves differently and
Methane Chemical Element Model Structure Stock Vector Illustration of

Bacteria that consume methane gas (CH 4) to produce methanol (CH 3 OH) using dioxygen (O 2) must break two chemical bonds: the bond holding the two oxygen atoms together, and one of the extremely.
Methane harms ozone layer 80 times more than Carbon dioxide Kenya Current
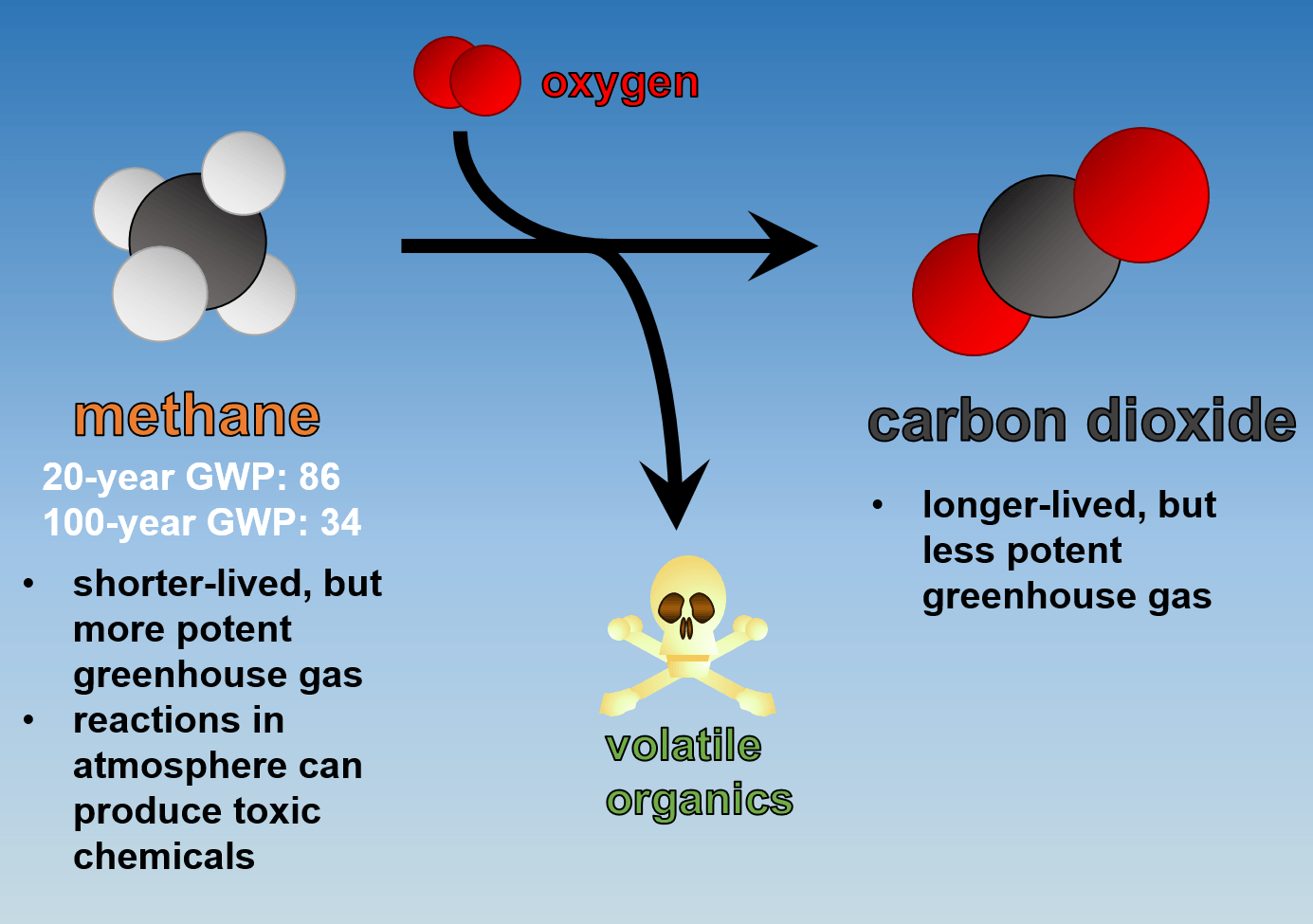
For example, in methane (CH 4 ), carbon forms covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms. Each bond corresponds to a pair of shared electrons (one from carbon and one from hydrogen), giving carbon the eight electrons it needs for a full outer shell. Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are organic molecules consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen.
Methane (CH4) Natural Gas Molecule, Flat Icon Style. Atoms Shown As
. One molecule of methane contains one carbon atom, surrounded by four hydrogen atoms. Methane is a greenhouse gas , and is produced by cows and landfill (waste) sites. Methane from farms.
Rendu 3D de la structure moléculaire du méthane — Photographie oorka5

The methane atoms decompose into carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrogen (H2), the same way it is processed naturally but at a rate that's roughly 100 million times faster in the.
Chapter 16 Section A Hydrocarbons

Methane is a simple gas, a single carbon atom with four arms of hydrogen atoms. Its time in the atmosphere is relatively fleeting compared to other greenhouse gases like CO 2 —any given.
Methane Molecule, with Transparent Balls of Atoms Stock Illustration
Methane ( US: / ˈmɛθeɪn / METH-ayn, UK: / ˈmiːθeɪn / MEE-thayn) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH4 (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas.
Electron Dot Diagram For Methane

The chlorine atoms then steal a hydrogen atom from the methane, which then falls apart and decomposes. The chlorine product (hydrochloric acid) is captured and subsequently recycled in the chamber.
Methane Exposure and It's Effects

The decomposition of methane (CH 4) is a catalytically important reaction in the production of syngas that is used to make a wide spectrum of hydrocarbons and alcohols, and a principal carbon.