
Human eye ball crosssection 3D model TurboSquid 1376280
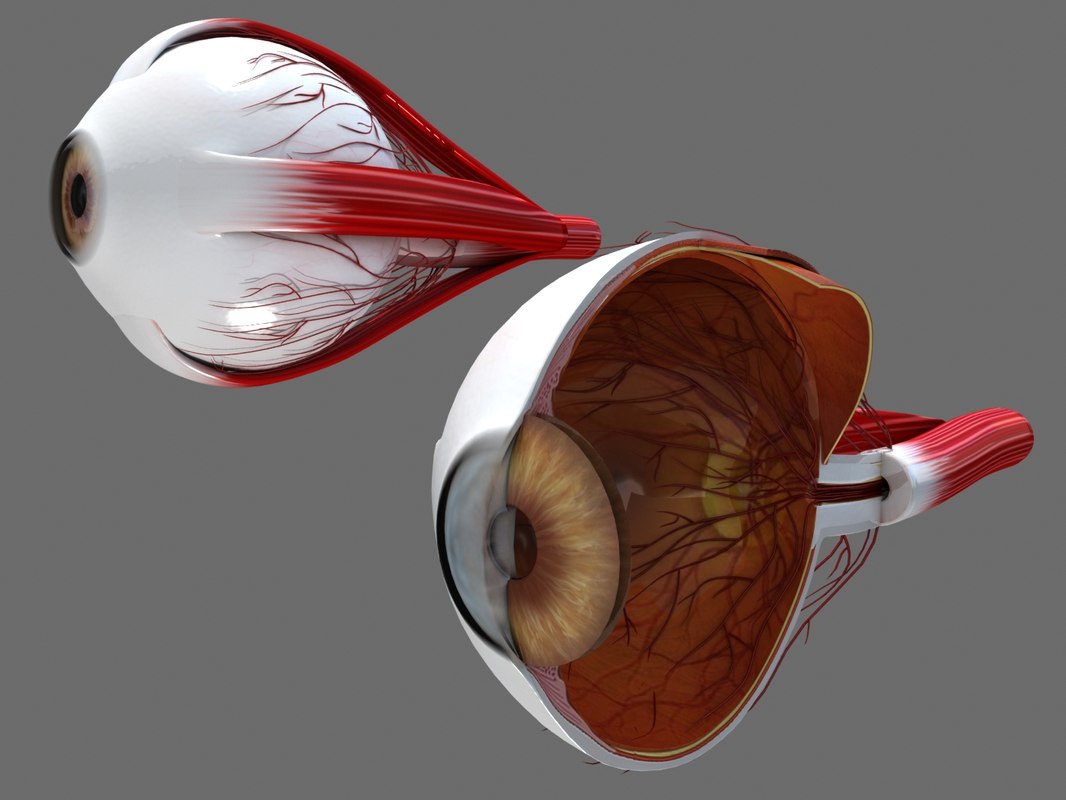
Fig. 2. Sagittal section of the adult human eye. A cross-sectional view of the eye shows: Three different layers. The external layer, formed by the sclera and cornea; The intermediate layer, divided into two parts: anterior (iris and ciliary body) and posterior (choroid) The internal layer, or the sensory part of the eye, the retina
Cross Section Of Human Eye Digital Art by Stocktrek Images Pixels

iStock Human Eye Anatomy Stock Illustration - Download Image Now - Eye, Cross Section, Sports Ball Download this Human Eye Anatomy vector illustration now. And search more of iStock's library of royalty-free vector art that features Eye graphics available for quick and easy download. Product #: gm648039286 $12.00 iStock In stock
Human Eye Png Eye Ball Cross Section, Transparent Png , Transparent Png Image PNGitem
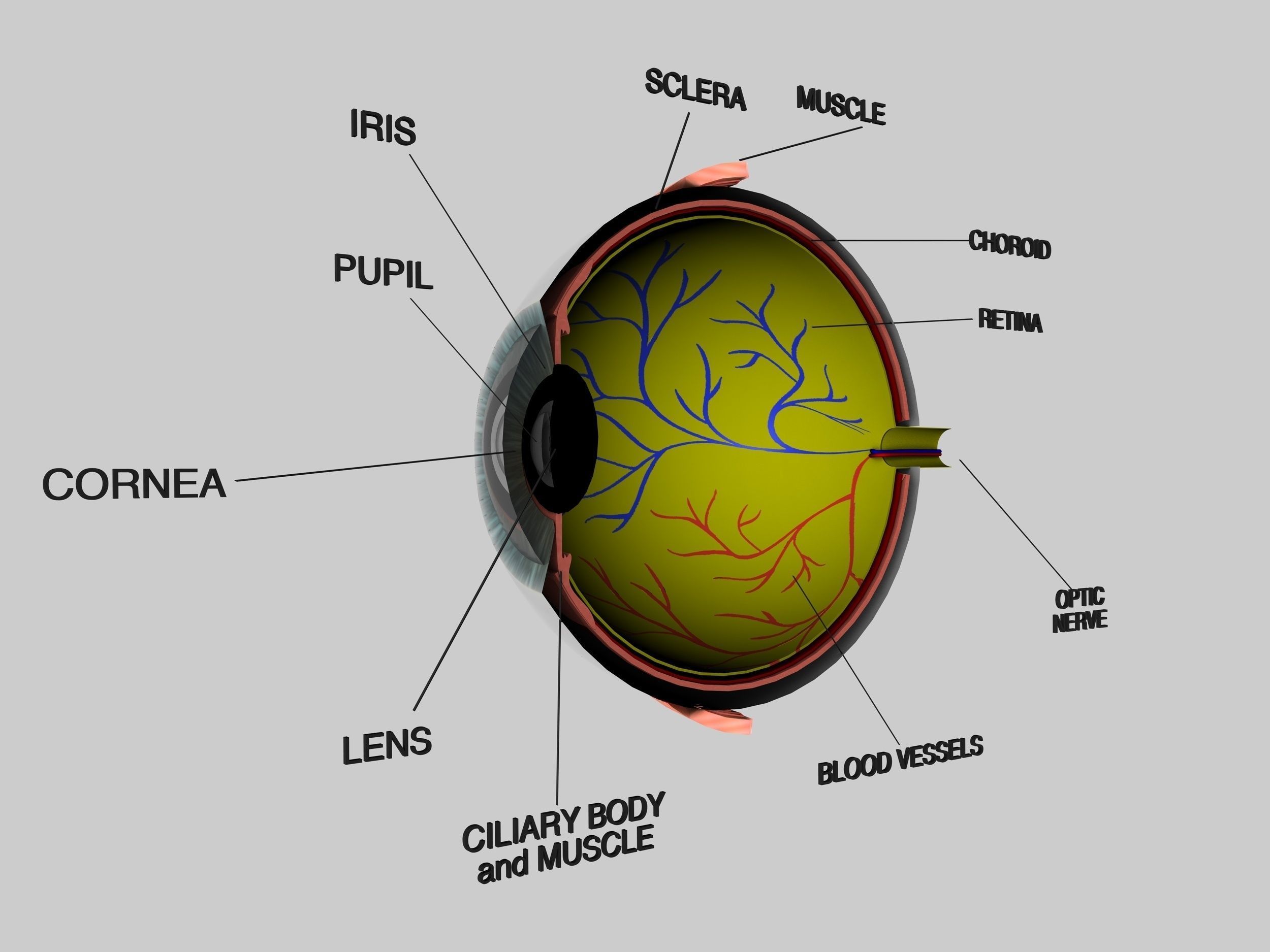
A cross-sectional view of the eye shows : Three different layers: The external layer, formed by the sclera and cornea. The. The sagittal section of the eye also reveals the lens, which is a transparent body located behind the iris. The lens is suspended by ligaments (called zonule fibers) attached to the anterior portion of the ciliary body..
eye cross section Discovery Eye Foundation

Cross Section of an EyeballThe eyeball has three major coats-the smooth, protective outer sclera, the middle, pigmented choroid and the inner, light-sensitiv.
Human Eye Cross Section Eyeball 3D Model OBJ 3DS FBX C4D DXF STL
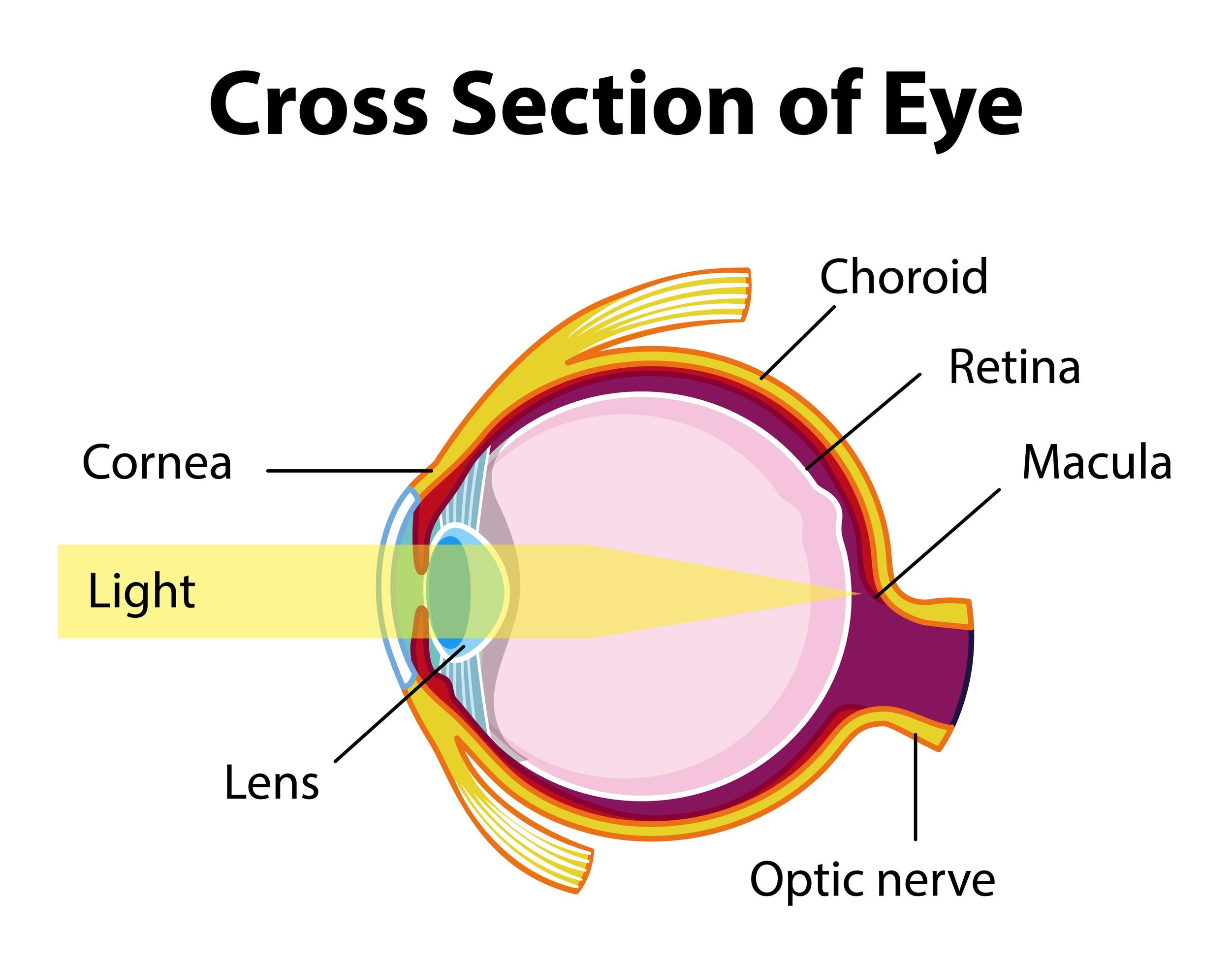
Representation of a horizontal section of the eyeball reveals its three coats: (1) external or fibrous coat (sclera and cornea); (2) middle or vascular coat (choroid, ciliary body, and iris); and (3) internal or retinal layer. The four refractive media are the cornea, the aqueous humor in the anterior chamber, the lens, and the vitreous body.
Human eye anatomy with cross section of eye diagram 1783141 Vector Art at Vecteezy
This is a cross-sectional study of patients with clinically-significant dry eye, suspected glaucoma (controls), glaucoma, or cataracts.. The ROC curve constructed from the final model's ability to predict a diagnosis of dry eye from glaucoma had a cross-validated mean AUC of 0.93 (cross-validated SD = 0.026), with a sensitivity of 89% and.
Anatomy of the Eye Human Eye Anatomy Owlcation
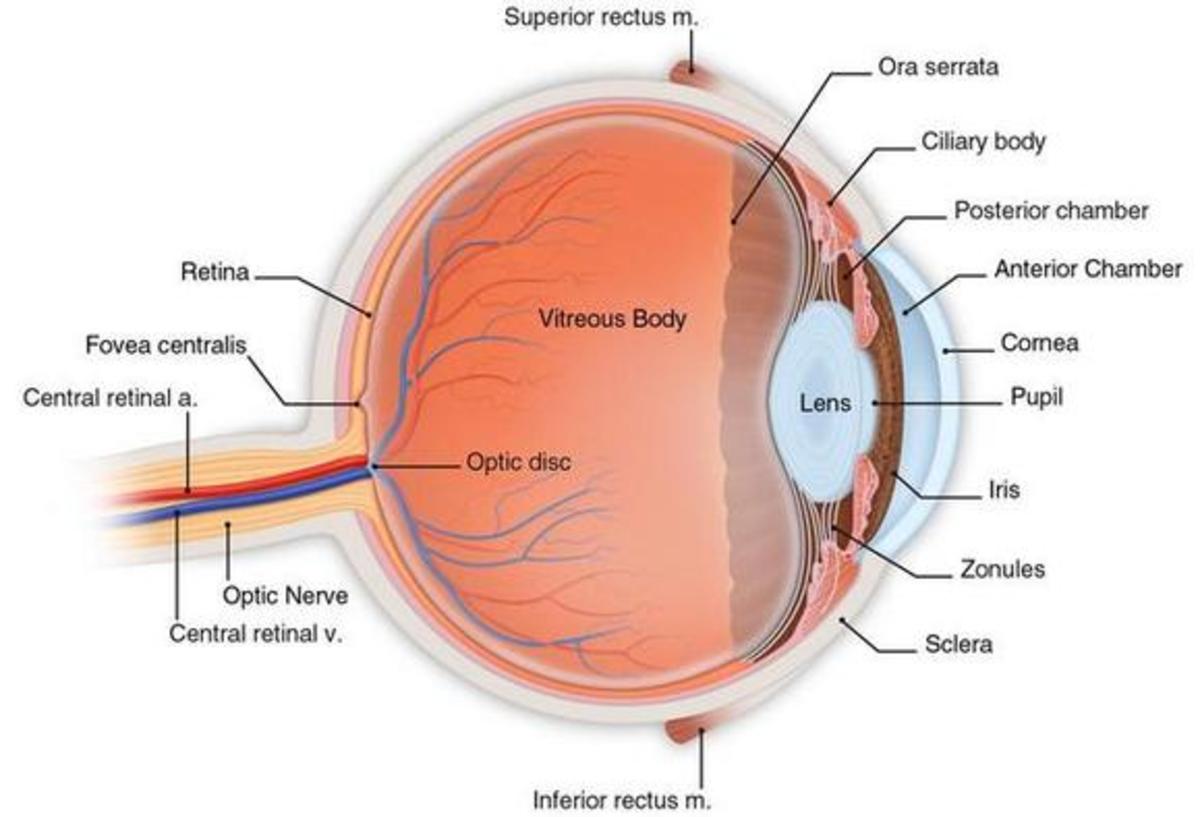
On the cross-section of the eye, we can identify the two chambers of the eyeball filled with the aqueous humor; anterior and posterior. The anterior chamber of eyeball is found between the cornea and iris. The posterior chamber of eyeball is more of a slit-like cavity, found between the iris and lens. Fascial sheath (Tenon's capsule)
Eyeball, cross section, illustration Stock Image C039/2362 Science Photo Library

Cross-section of the eye The zonules of Zinn keep the lens suspended, and the muscles of the ciliary body focus the lens. The ciliary body also secretes aqueous humor, which fills the anterior and posterior chambers, passes through the pupil into the anterior chamber, and drains primarily via Schlemm's canal.
Human Eye Cross Section Eyeball 3D Model OBJ 3DS FBX C4D DXF STL

Human eye anatomy diagram, medical illustration. Isolated on a white bacground. Eye anatomy. Rod cells and cone cells. Eye anatomy. Rod cells and cone cells. The arrangement of retinal cells is shown in a cross section. Vector diagram for your design, educational, biological, science and medical use.
Human Eye Cross Section Eyeball 3D Model OBJ 3DS FBX C4D DXF STL

Cross-section of the eye. The zonules of Zinn keep the lens suspended, and the muscles of the ciliary body focus the lens. The ciliary body also secretes aqueous humor, which fills the anterior and posterior chambers, passes through the pupil into the anterior chamber, and drains primarily via the Schlemm canal. The iris regulates the amount of.
3d illustration of a cross section of the human eye with explanations and inscription Stephan
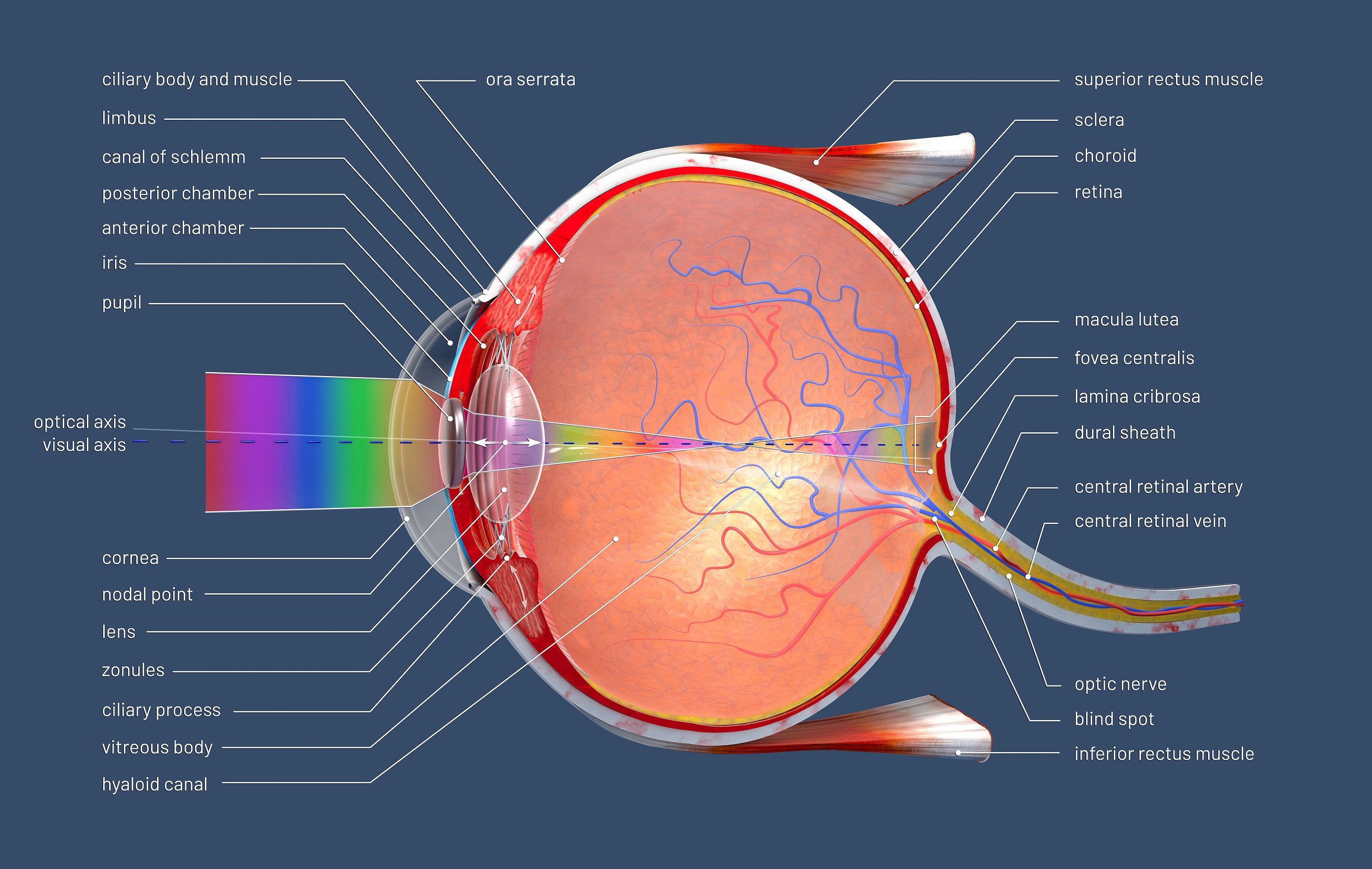
human eye, in humans, specialized sense organ capable of receiving visual images, which are then carried to the brain.. Anatomy of the visual apparatus Structures auxiliary to the eye The orbit. The eye is protected from mechanical injury by being enclosed in a socket, or orbit, which is made up of portions of several of the bones of the skull to form a four-sided pyramid, the apex of which.
Human Eye Anatomy 3D Model Cross Section with all Eye parts Ready for Renderings, 3D Printings

Dry eye syndrome is the most common eye disease, and if untreated, it can cause corneal ulcerations, scarring, and even perforation.. is an approximately 1.5mm area of specialized avascular retina that can be identified as a depression in the retina in cross-section. The foveola is the central floor of the fovea, approximately 0.35mm in.
Human eye cross section Royalty Free Vector Image
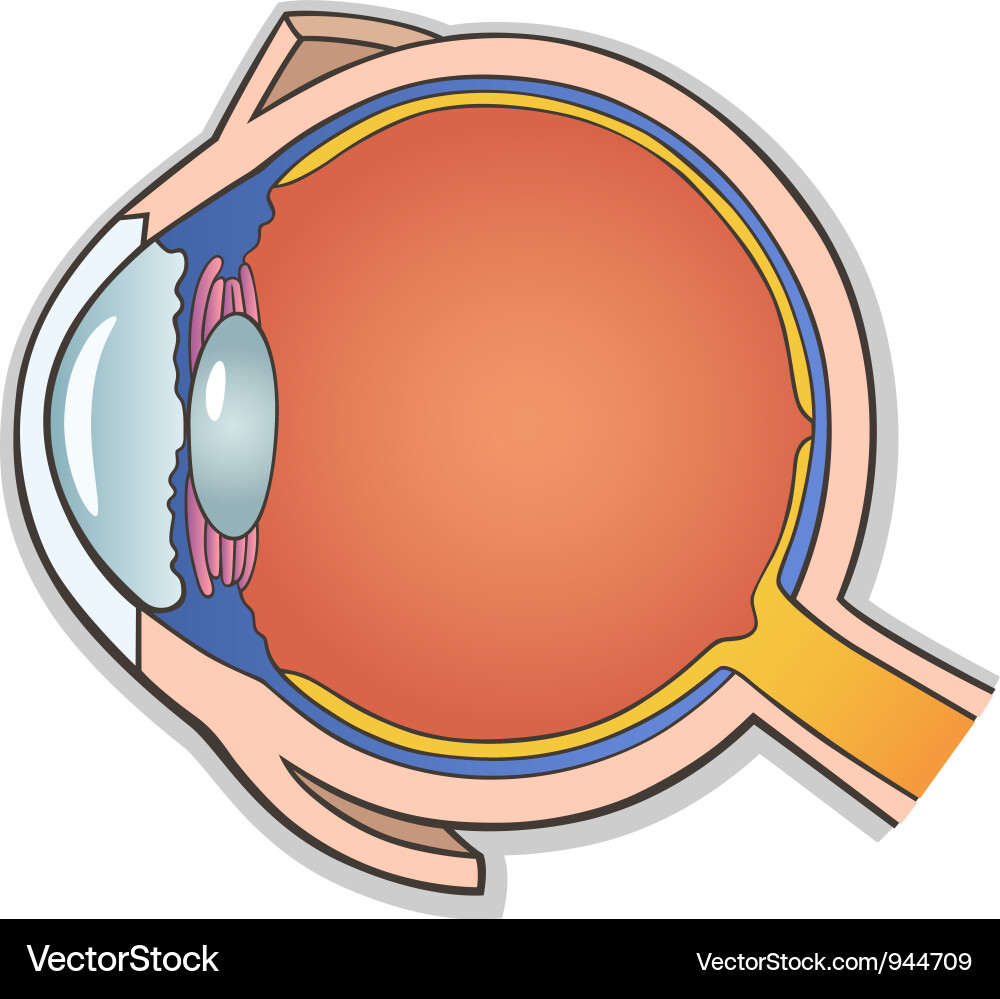
Ciliary body. The part of the eye that produces aqueous humor. Cornea. The clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. Iris. The colored part of the eye. The iris is partly responsible for regulating the amount of light permitted to enter the eye. Lens (also called crystalline lens).
Human Eye Cross Section Eyeball 3D Model OBJ 3DS FBX C4D DXF STL

Cross section of the human eyeball viewed from above. Dave Carlson / CarlsonStockArt.com. Iris. The choroid continues at the front of the eyeball to form the iris. The iris is a flat, thin, ring-shaped structure sticking into the anterior chamber. This is the part that identifies a person's eye colour.
Montessori Materials Cross Section Eye Model
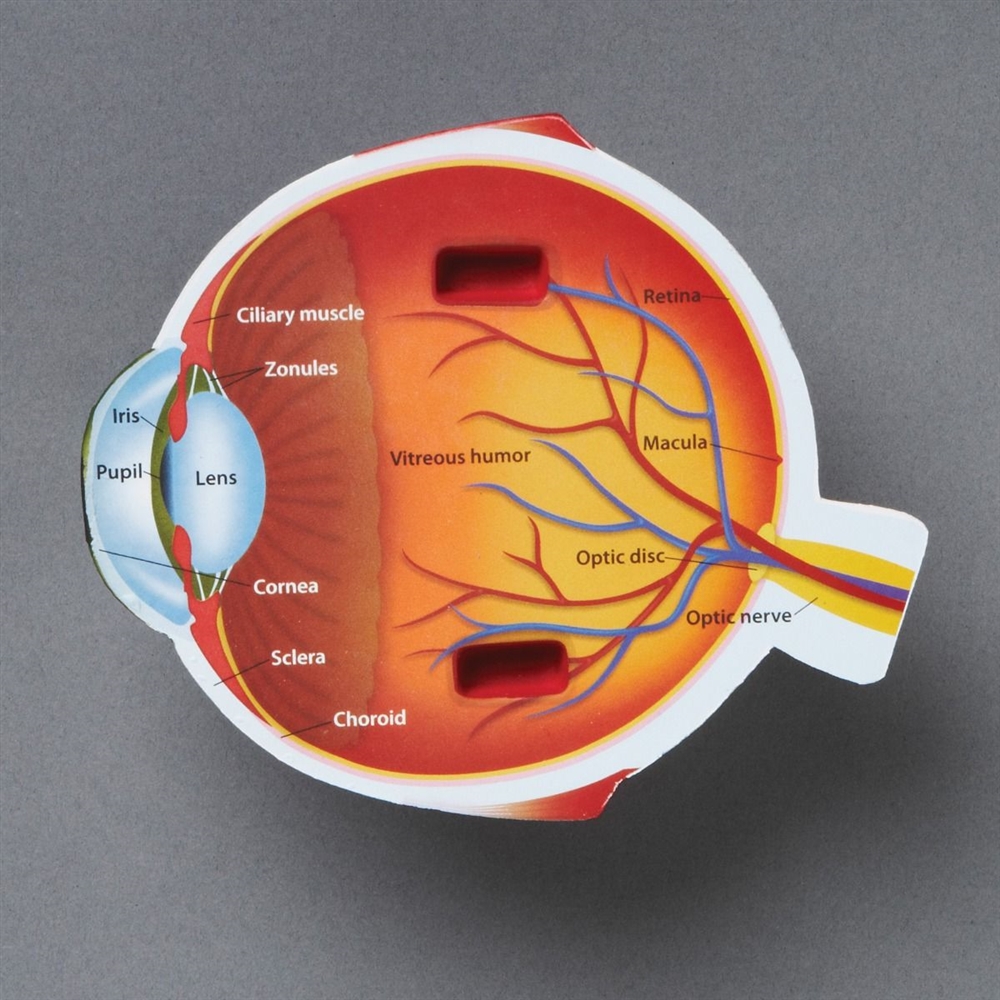
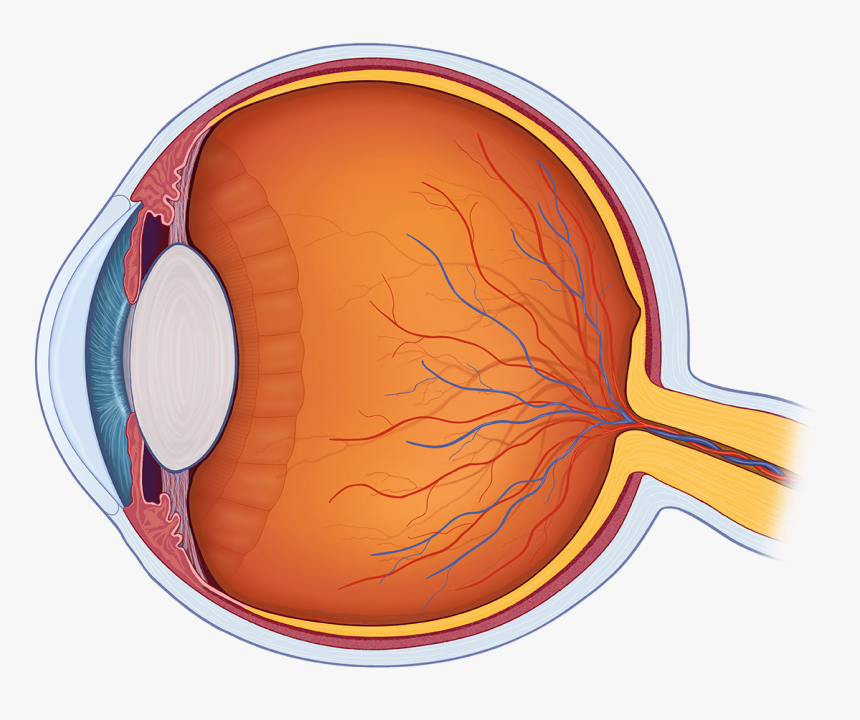
Cross section of the eye. Note that the course of light travels through the cornea, pupil, and crystalline lens (becomes the cataract) to the retina and then to the brain through the optic nerve. An official website of the United States government
Crosssection through the human eye — Science Learning Hub

Cross-section of the eye. The zonules of Zinn keep the lens suspended, and the muscles of the ciliary body focus the lens. The ciliary body also secretes aqueous humor, which fills the anterior and posterior chambers, passes through the pupil into the anterior chamber, and drains primarily via the Schlemm canal. The iris regulates the amount of.