
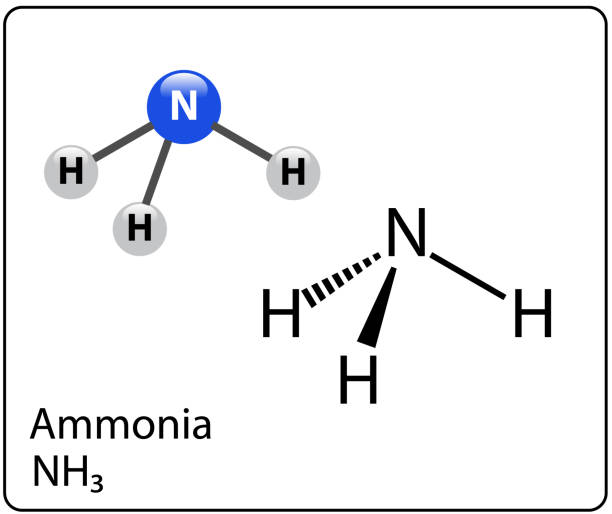
Ammonia Chemical Formula, NH3 Uses, Application, Valency

Solid NH 3 Two visible states of NH 3 Ammonia is a colourless gas with a characteristically pungent smell. It is lighter than air, its density being 0.589 times that of air.
3.9. Dipoles. Polar and nonpolar Molecules Mr. Ehinger's Chemistry
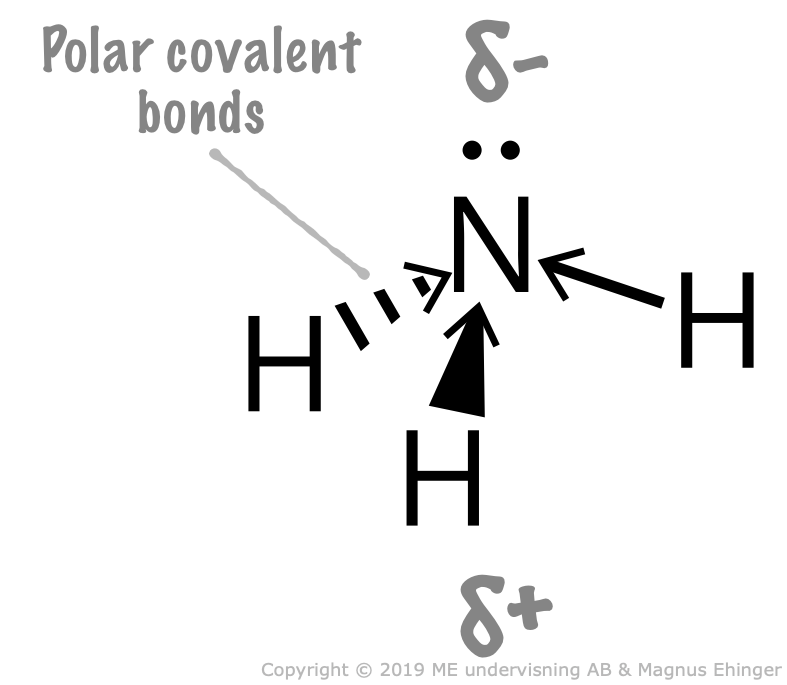
Polar molecules are molecules that have a permanent dipole moment. This permanent dipole moment is an indication of the molecule's polarity. The polarity of a molecule is determined by the distribution of electric charge within it. The electrons.
Polar Molecule Definition and Examples Biology Dictionary

NH3 is a polar molecule because it has three nitrogen-hydrogen bond dipoles that do not cancel out. In each bond, nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen. The polarity comes from the unequal distribution of charges among both nitrogen and hydrogen atoms. Name of molecule. Ammonia (NH3) Bond Angles. 107.3 degrees.
Is NH3 Polar or NonPolar? (Ammonia) Yes Dirt

ammonia (NH 3), colourless,. It is a polar molecule and is highly associated because of strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The dielectric constant of ammonia (22 at −34 °C [−29 °F]) is lower than that of water (81 at 25 °C [77 °F]), so it is a better solvent for organic materials.
Is NH3 Polar or Nonpolar? Techiescientist

Ammonia has a molecular mass of 17.031 g/mol, maintains a density of 0.73 kg/cubic meter, has a boiling point of -28.01 degrees Fahrenheit, and a melting point of -107.9 degrees Fahrenheit. It is a stable binary hydride and is considered the simplest of the pnictogen hydrides.
Is NH3 Polar or Nonpolar? (Ammonia) YouTube

If you look at the Lewis structure for NH3 we can see that it is not a symmetrical molecule. However, to determine if NH3 is polar we need to look at the mo.
Is NH3 (ammonia) polar or nonpolar? YouTube
Yes, Ammonia is a polar molecule. The polarity of nh3 is mostly depicted by the electron density difference between nitrogen and hydrogen atoms. The three N-H bonds each having separate dipoles makes ammonia a polar compound. The lewis structure of ammonia perfectly explains the polarity of nh3 as the three are a total of 8 valence electrons (5.
Determining whether a molecule is polar Do ammonia, NH3 1
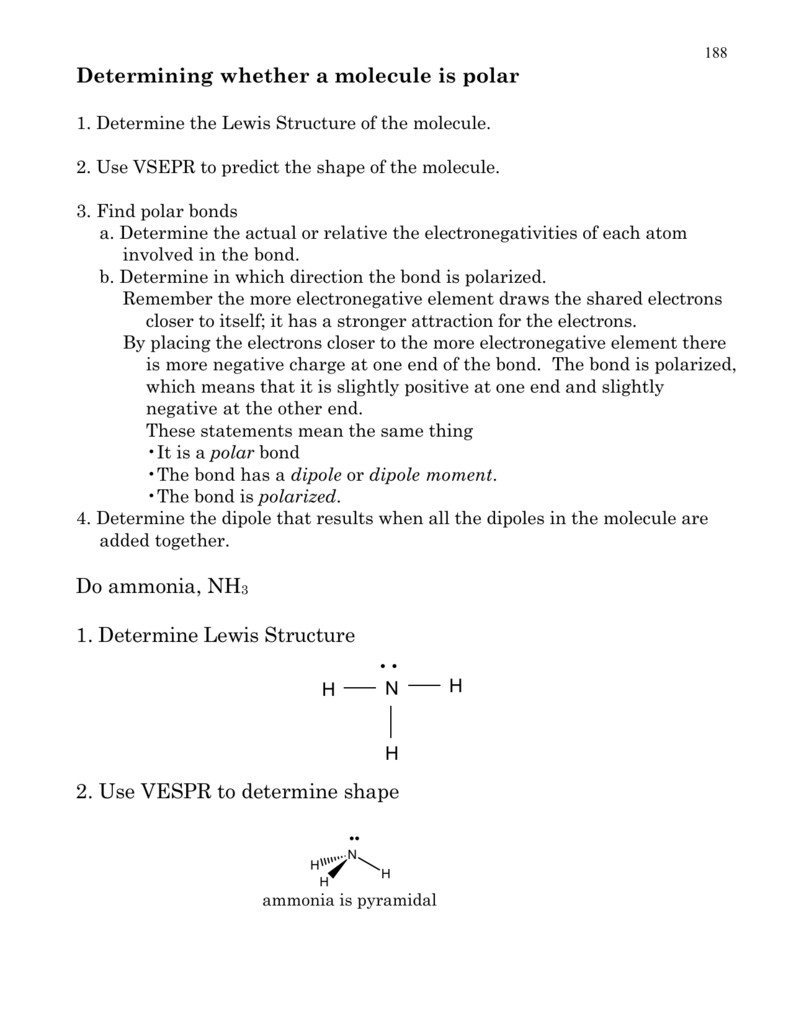
Ammonia: Propane, C 3 H 8: Bromine, Br 2: Solution. Ammonia is polar. When properly rotated, one can see that the nitrogen atom sits on a different plane than the hydrogen atoms . All of the arrows point in the direction of the nitrogen atom, giving it a net direction (the strength and direction of the arrows do not cancel).
PPT Electronegativity & Polarity PowerPoint Presentation, free
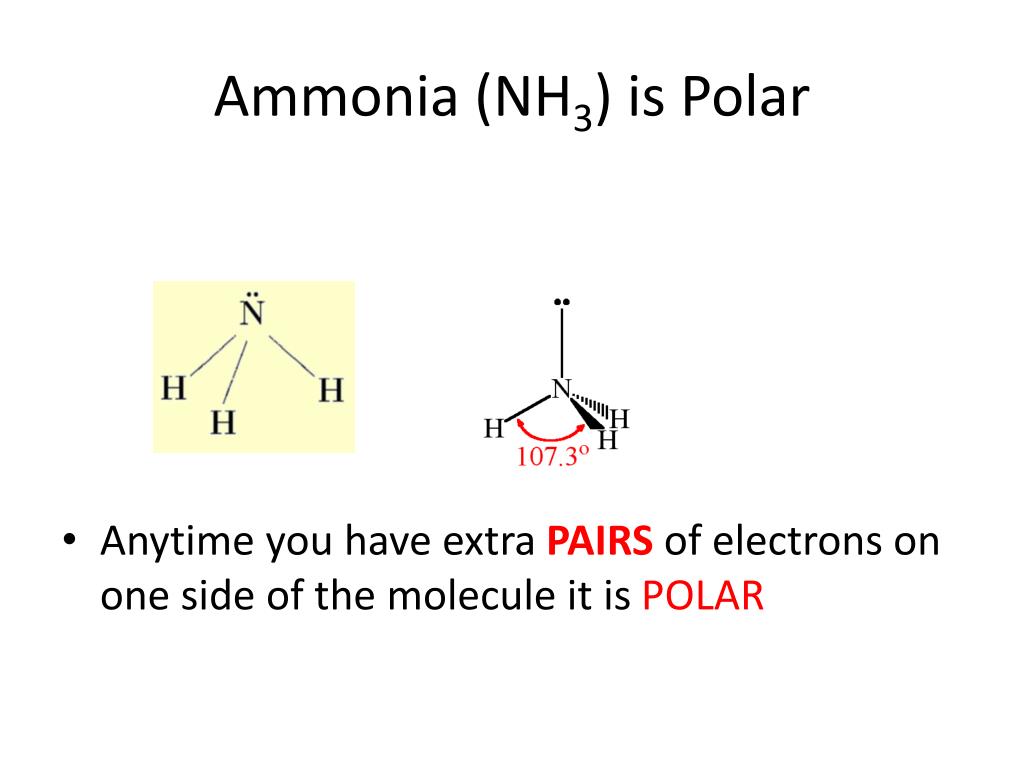
ammonia is pyramidal 189 Electronegativity of N = 3.0, H = 2.1, so electrons in each bond are closer to the N than the H. Determine the resultant dipole. is the positive end. How about CH2Cl2 Determine Lewis Structure Use VSEPR to determine shape Determine the bond polarity The dipoles cancel out. No dipole moment.
Is NH3 polar? How To Discuss
0:00 / 1:05 Is NH3 (ammonia) polar or nonpolar? Mentor Center 910 subscribers Subscribe Subscribed Share 13K views 3 years ago Chemistry videos Hey everyone, welcome to the Mentor Center! In.
Is NH3 (Ammonia) Polar or NonPolar? Lewis Structure YouTube

When you place a molecule with an electric dipole in an electric field, a force acts to turn the molecule so that the positive and negative ends line up with the field. The magnitude of the turning force is given by the formula. µ = q × d. where q is the amount of charge and d is the distance between the two charges. µ is the turning moment.
Is NH3 Polar or Nonpolar? Techiescientist

NH3 (or Ammonia) is a POLAR molecule because the Nitrogen (N) present in the molecule is more electronegative, which causes the partial positive (ẟ+) and partial negative (ẟ-) charge to appear on the molecule. These ẟ+ and ẟ- charges are responsible to make the entire NH3 molecule polar.
Is NH3 Polar or Nonpolar?Is Ammonia a Polar or Nonpolar Molecule?

Examples of such molecules include hydrogen sulfide, H 2 S (nonlinear), and ammonia, NH 3 (trigonal pyramidal). To summarize, to be polar, a molecule must: Contain at least one polar covalent bond. Have a molecular structure such that the sum of the vectors of each bond dipole moment does not cancel. Properties of Polar Molecules
[Solved] explain why the ammonia molecule is polar while aluminum
is a separation of leading to a electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry.
Covalent bonding
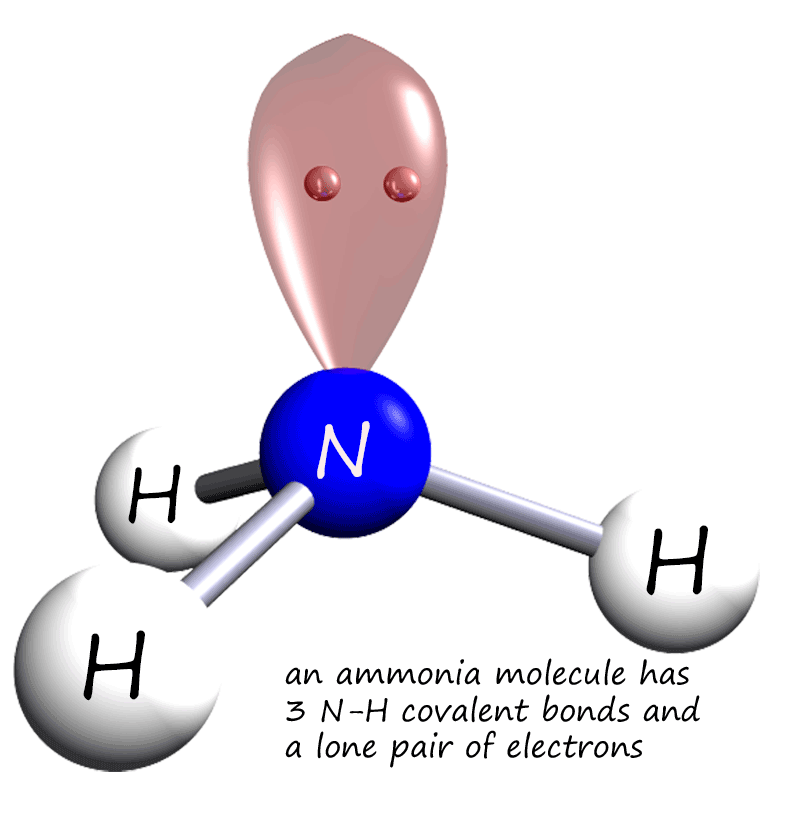
Ammonia or NH3 is a polar molecule as there is a large difference of electronegativities between Nitrogen and Hydrogen along with the asymmetric shape of the molecule. The uneven dispersion of electric charges in the molecule makes it a polar molecule. Priyanka To read, write and know something new every day is the only way I see my day!
PPT Polar Bonds and Molecules PowerPoint Presentation ID544532
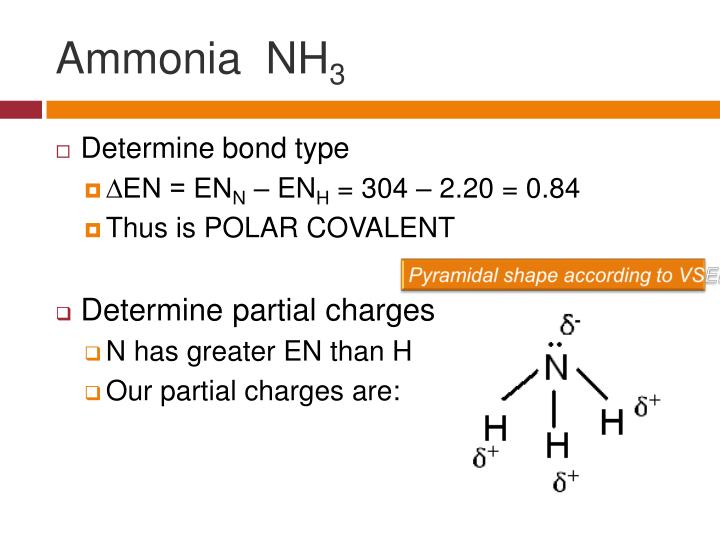
To summarize, ammonia is a polar molecule because its electron geometry is trigonal pyramidal and the dipoles of N-H bonds do not cancel out. Remember, the net dipole of the molecule is the vector sum of all the dipoles and here it equals zero because the bonds are equivalent and pointing in opposite directions.