
Tibia Anterior And Posterior View
The soleus is a muscle within the superficial compartment of the posterior leg. It is a flat muscle located underneath the gastrocnemius, and gets its name from its resemblance to a sole - a flat fish. Attachments: Originates from the soleal line of the tibia and proximal fibula.
Tibial Anatomy
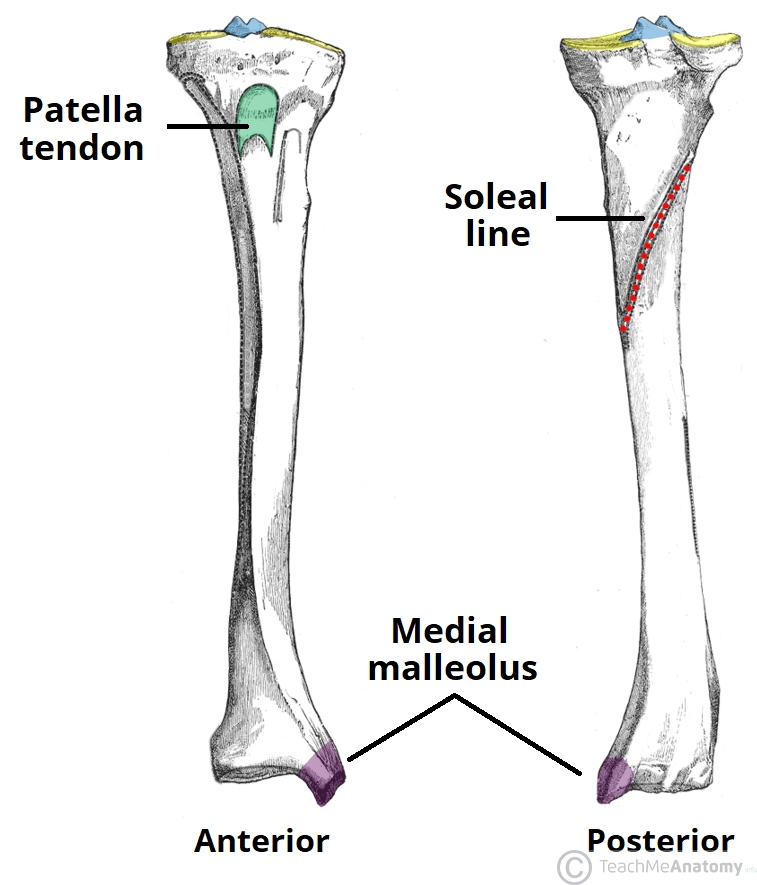
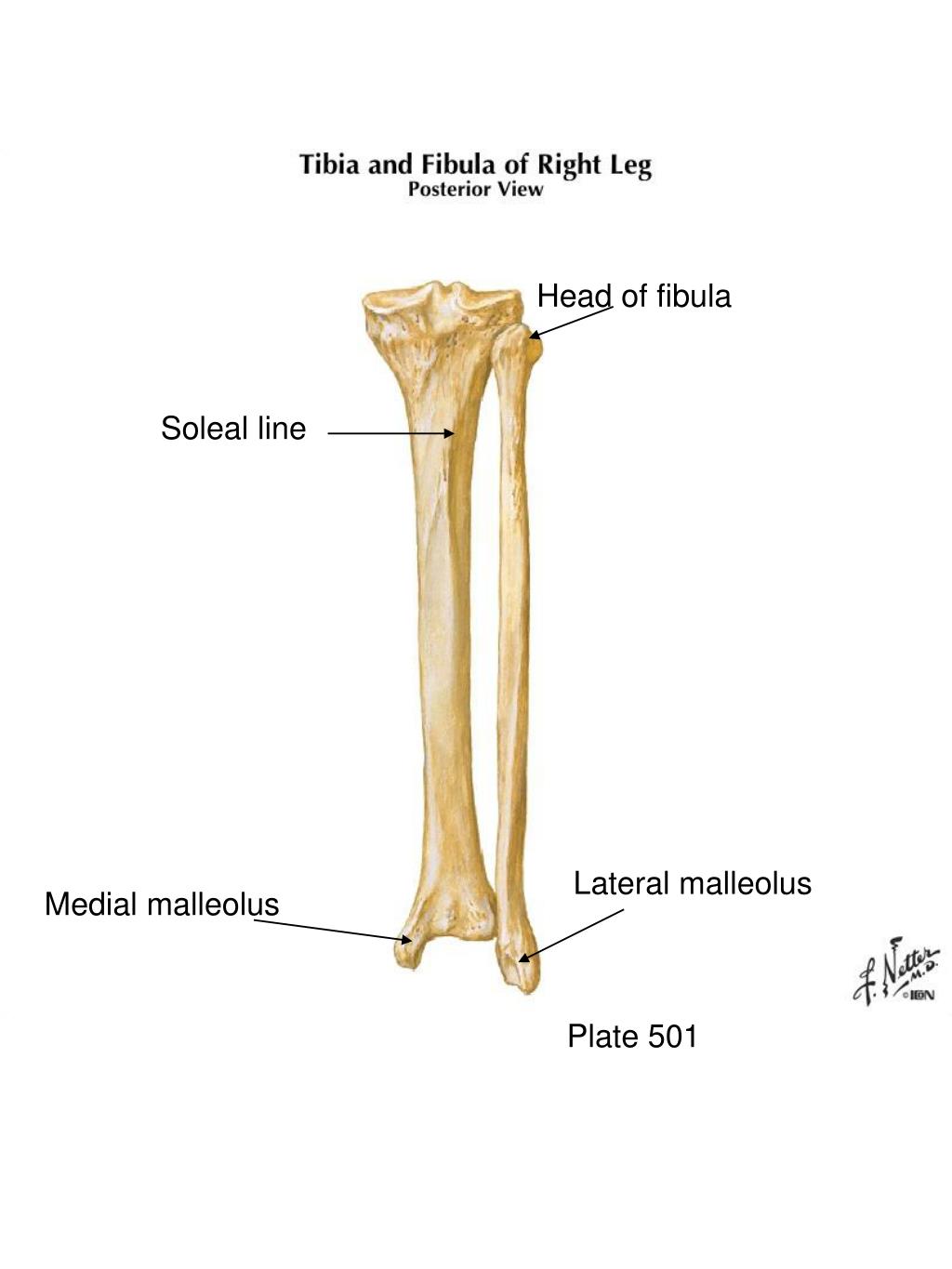
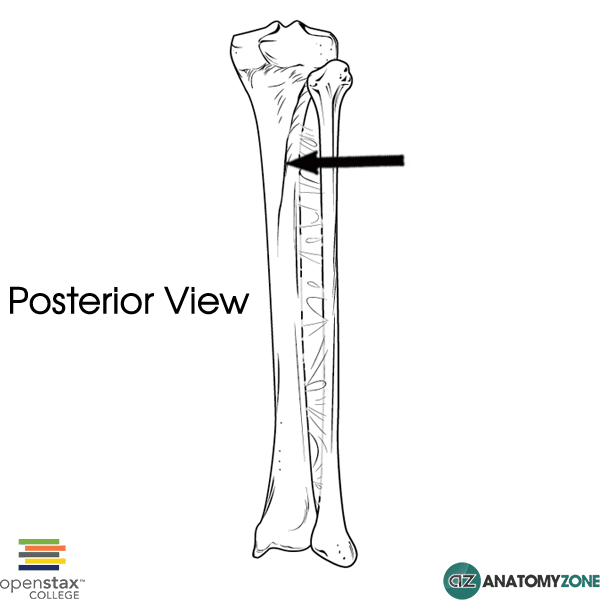
On the posterior aspect of the tibia, the soleal line runs diagonally in a distal-to-medial direction across the proximal third of the tibia. [2] Lateral Distal End The lateral aspect of the distal tibia forms the fibular notch, creating an articulation between the distal tibia and fibula, the distal tibiofibular joint. [3]
Tibia Anatomy Bony Landmarks & Muscle Attachment » How To Relief
The soleus muscle originates from the head and upper third of the posterior border of the fibula, soleal line and middle third of the medial border of the tibia and tendinous arch between the fibula and tibia. Insertion. The soleus joins with the gastrocnemius, and both muscles form a common tendon called the calcaneal or Achilles tendon that.
diagram of the tibia

An unusually prominent soleal line (a normal anatomic variant) may mimic periosteal reaction along the posterior margin of the proximal tibial shaft. This area of pseudoperiostitis is differentiated from hyperostoses arising from the anterior tibial tubercle and the interosseous membrane. It is always associated with normal, undisturbed architecture of the underlying bone.
Tibia and Fibula Bones Posterior View
The soleus muscle arises from the soleal line on the dorsal surface of the tibia, medial border of the tibia, head of the fibula, and posterior border of the fibula. Part of the fibers arises from the tendinous arch of the soleus, which spans between the tibia and fibula and arches over the popliteal vessels and tibial nerve.
Tibia (Shin Bone) Definition, Location, Anatomy, & Diagrams
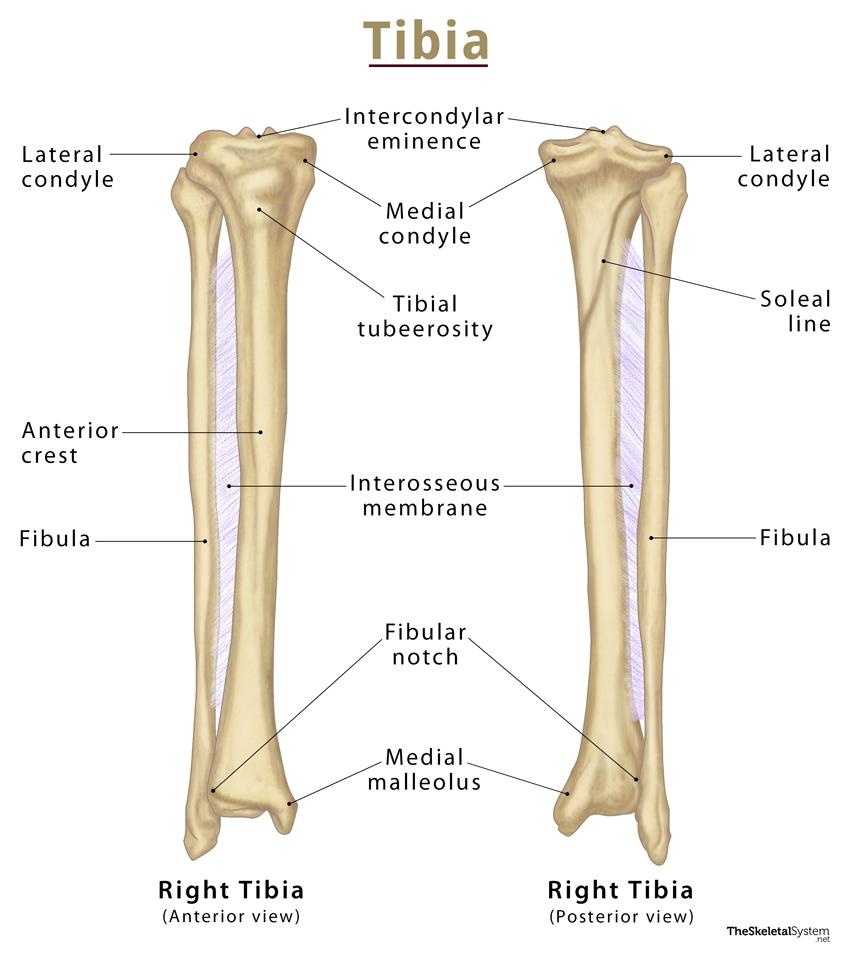
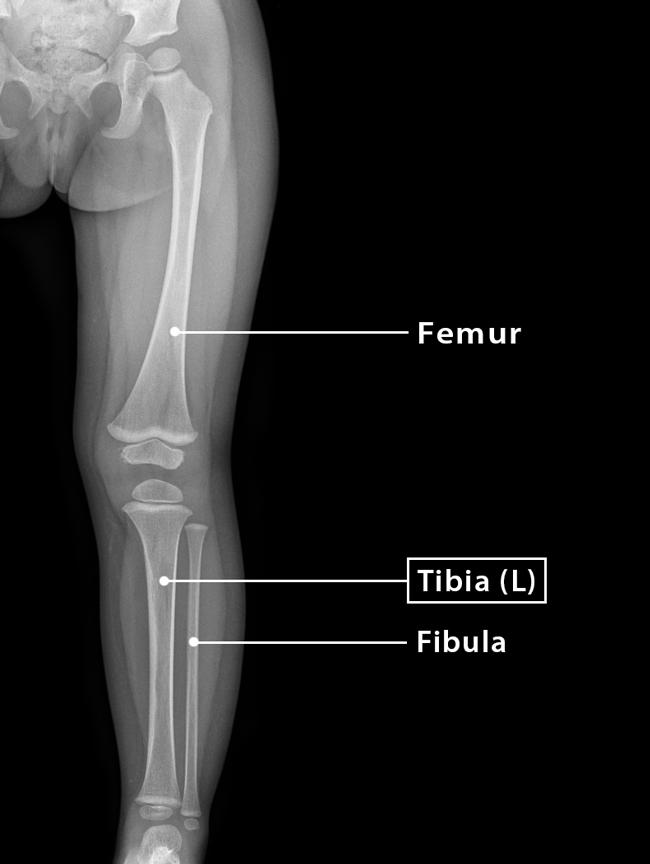
The tibia is one of two bones that comprise the leg. [1] As the weight-bearing bone, it is significantly larger and stronger than its counterpart, the fibula. The tibia forms the knee joint proximally with the femur and forms the ankle joint distally with the fibula and talus.
Tibia osteology (posterior view) Diagram Quizlet

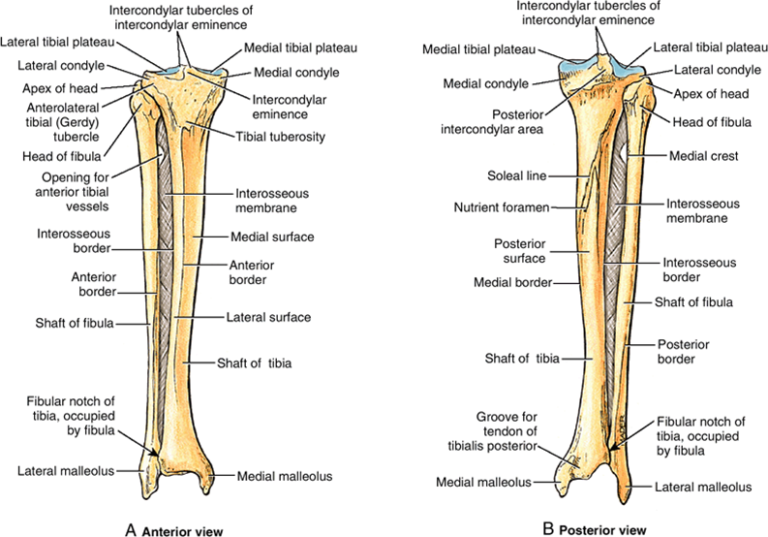
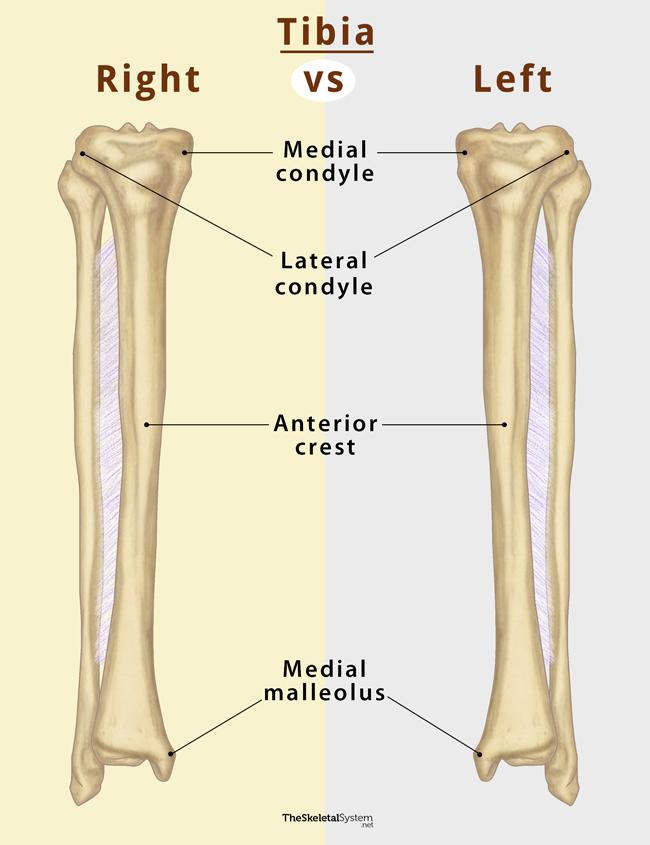
It features a bony ridge called the soleal line. The line crosses this surface diagonally and eventually blends with the medial border of the tibia. Distal Tibia and its Bony Landmarks. At the distal end, the tibia widens and appears rectangular in cross-section. It has two bony landmarks, the medial, malleolus, and fibular notch. 1.
Bones of the Lower Limb Anatomy and Physiology I

Definition The soleal line is a diagonal bony ridge that is located in the upper portion of the posterior surface of tibia. It is oriented downward and medially. Above the soleal line, the triangular region of the posterior surface of tibia serves as the point of origin for the popliteus muscle.
PPT Femur PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4013033
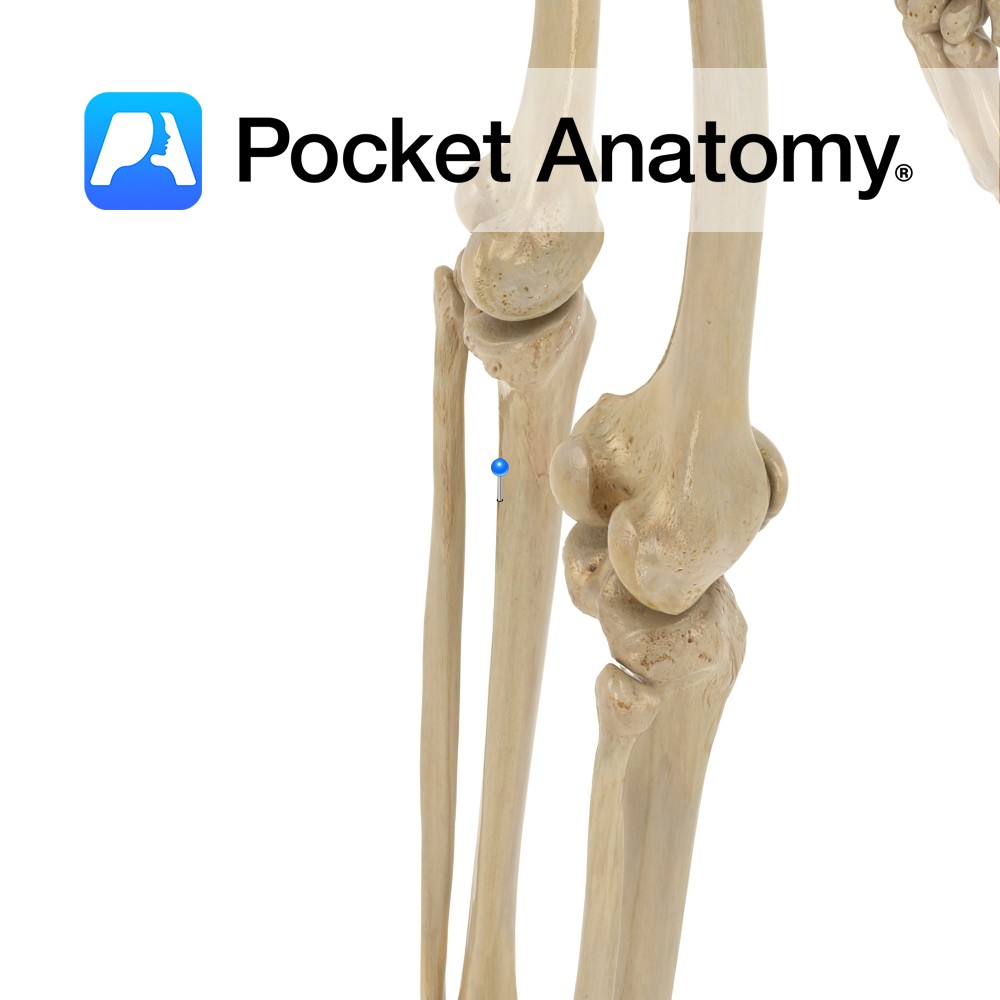
Last modified: 13 December 2020 The structure indicated is the soleal line of the tibia. The soleal line is an oblique line visible on the posterior surface of the tibia. The popliteus muscle inserts above the soleal line. Three other muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg take their origin, or part of their origin from the soleal line:
Tibia soleal line Pocket Anatomy
Origin: Fibula, medial border of tibia (soleal line) Insertion: Tendo calcaneus Artery: Sural arteries Nerve: Tibial nerve, specifically, nerve roots L5-S2 Action: Plantarflexion Antagonist: Tibialis anterior muscle Description: The Soleus is a broad flat muscle situated immediately in front of the Gastrocnemius. Itarises by tendinous fibers from the back of the head of the fibula, and from.
Tibia (Shin Bone) Definition, Location, Anatomy, & Diagrams
The soleal (popliteal) line is the rough ridge found on the proximal half of the posterior surface of tibia. It extends inferomedially from the fibular articular facet to the medial border of tibia. It provides an origin site for the soleus muscle, and an attachment site for the transverse intermuscular septum of leg. Complete Anatomy
Tibia Anatomy, Location, Structure and FAQs
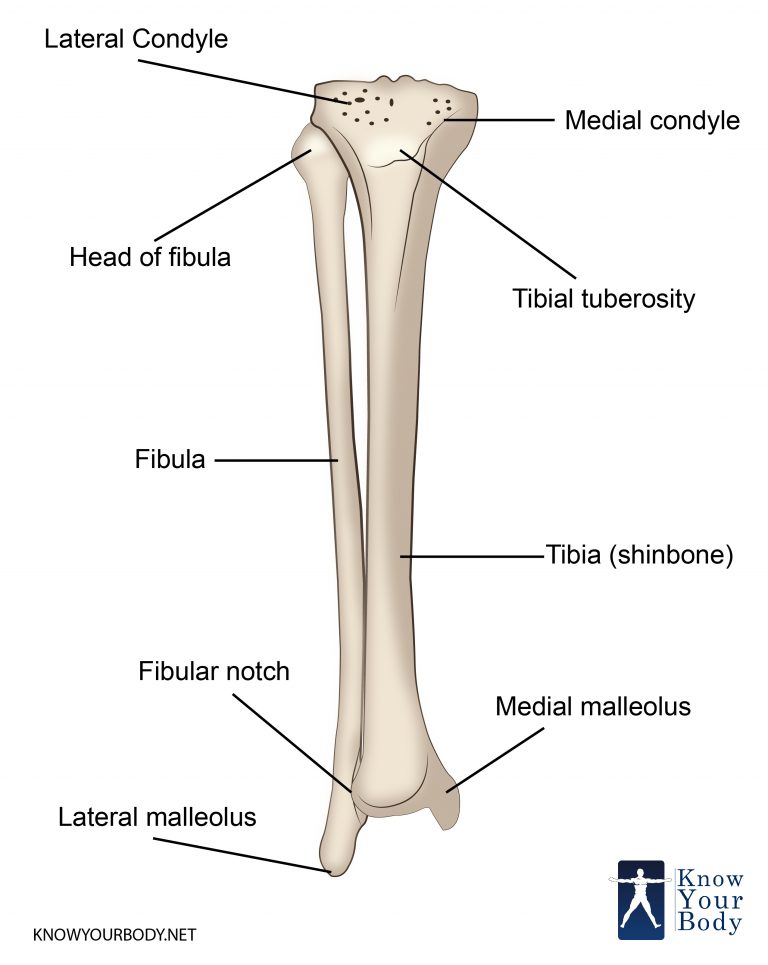
The tibia (plural: tibiae) is the largest bone of the leg and contributes to the knee and ankle joints. (shin- or shank-bone are lay terms). It is medial to and much stronger than the fibula, exceeded in length only by the femur. Gross anatomy Osteology
Tibia and Fibula (1) in 2023 Anatomy bones, Medical anatomy, Human

The soleal line is a prominent ridge on the posterior surface of the tibia. It extends obliquely downward from the back part of the articular facet for the fibula to the medial border, at the junction of its upper and middle thirds. Development The soleal line becomes more prominent between childhood and adulthood. [1]
Pin on Anatomy

The tibia or shinbone is the strongest bone in the human body. It may withstand the vertical load of more than 1000 kg *. * Quenneville C, et al. Injury tolerance criteria for short-duration axial impulse loading of the isolated tibia. The Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection, and Critical Care, 2011, 70 (1):E13-E18
PPT Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle on Lower Extremity PowerPoint

The fibula is a slender, cylindrical leg bone that is located on the posterior portion of the limb. It is found next to another long bone known as the tibia. A long bone is defined as one whose body is longer than it is wide. Like other long bones, the fibula has a proximal end (with a head and neck), a shaft, and a distal end.
Soleal Line AnatomyZone
The tibia (shin bone) is a long bone of the leg, found medial to the fibula. It is also the weight bearing bone of the leg, which is why it is the second largest bone in the body after the femur. Fun fact here is that 'tibia' is the Latin word for tubular musical instruments like the flute.