Bones Of The Skull Inferior Photograph by Evan Oto Pixels
Lateral view of the skull featuring the coronal, lambdoid, and squamous sutures. Image: "Skull sutures" by OpenStax College.License: CC BY 3.0 Major fontanelles Fontanelles Physical Examination of the Newborn are areas of connective tissue Connective tissue Connective tissues originate from embryonic mesenchyme and are present throughout the body except inside the brain and spinal cord.
Nasopharynx Radiology Key
The cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the brain case, or cranial vault (Figure 6.3.1 6.3. 1 ). The facial bones underlie the facial structures, form the nasal cavity, enclose the eyeballs, and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws.
axial skull coloring pages Google Search Skull anatomy, Anatomy

The cranium (also known as the neurocranium) is formed by the superior aspect of the skull. It encloses and protects the brain, meninges, and cerebral vasculature. Anatomically, the cranium can be subdivided into a roof and a base: Cranial roof - comprised of the frontal, occipital and two parietal bones. It is also known as the calvarium.
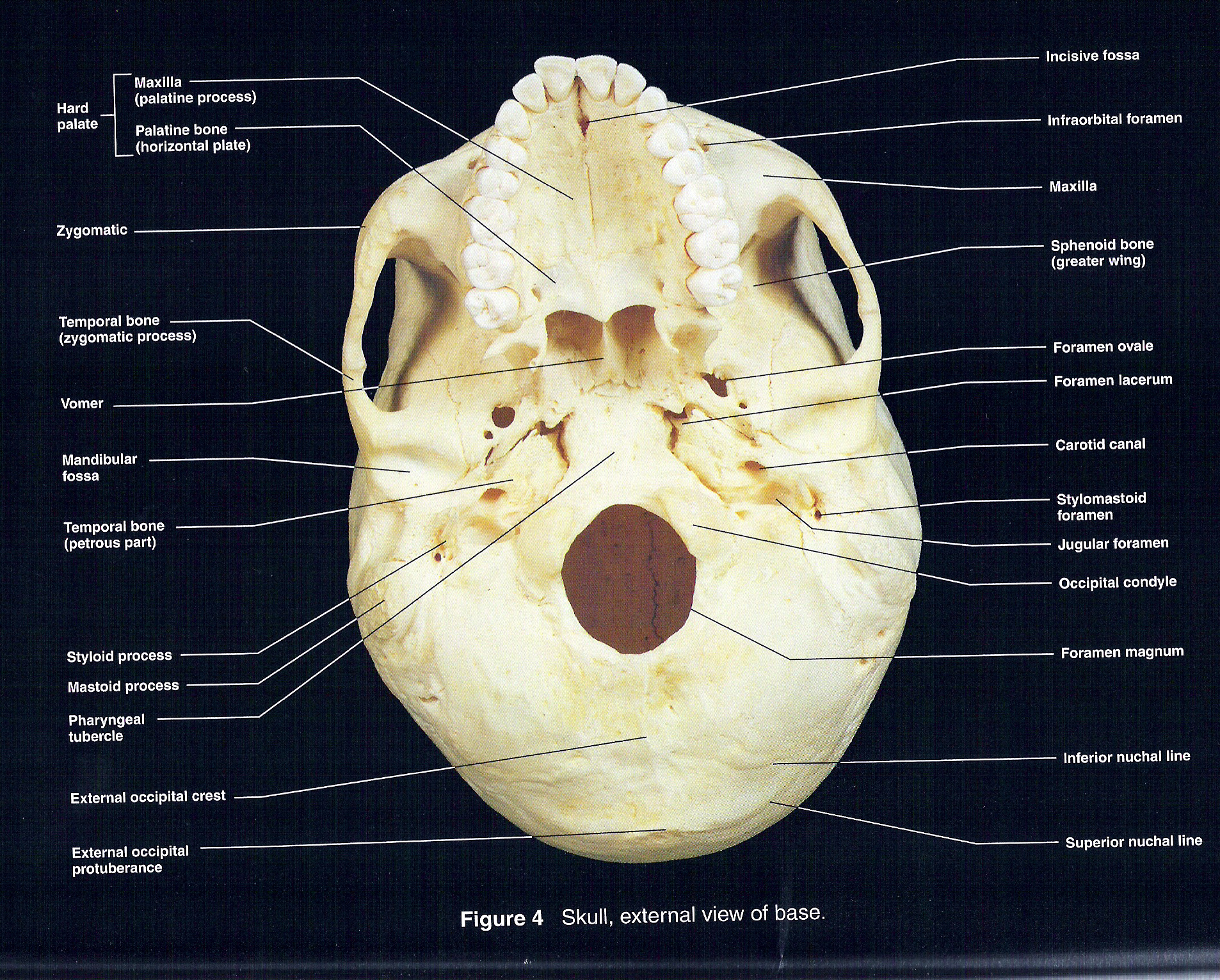
This image shows the superior and inferior view of the skull base. In

Human skeleton - Skull, Bones, Joints: The interior of the cranium shows a multitude of details, reflecting the shapes of the softer structures that are in contact with the bones. The internal surface of the vault is relatively uncomplicated. In the midline front to back, along the sagittal suture, the seam between the two parietal bones, is a shallow depression—the groove for the superior.
Skull, inferior view Human anatomy and physiology, Anatomy and

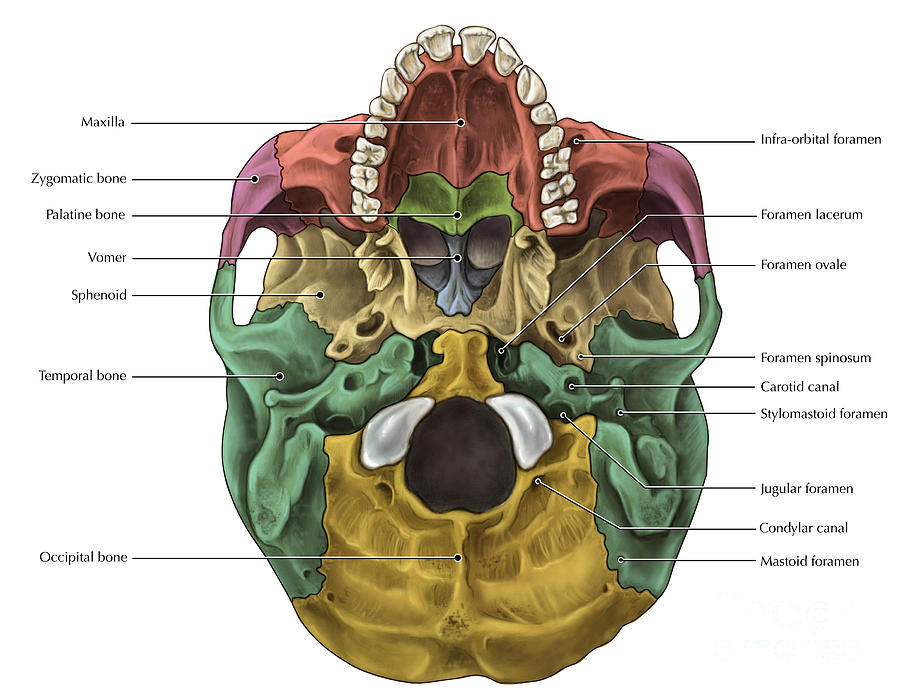
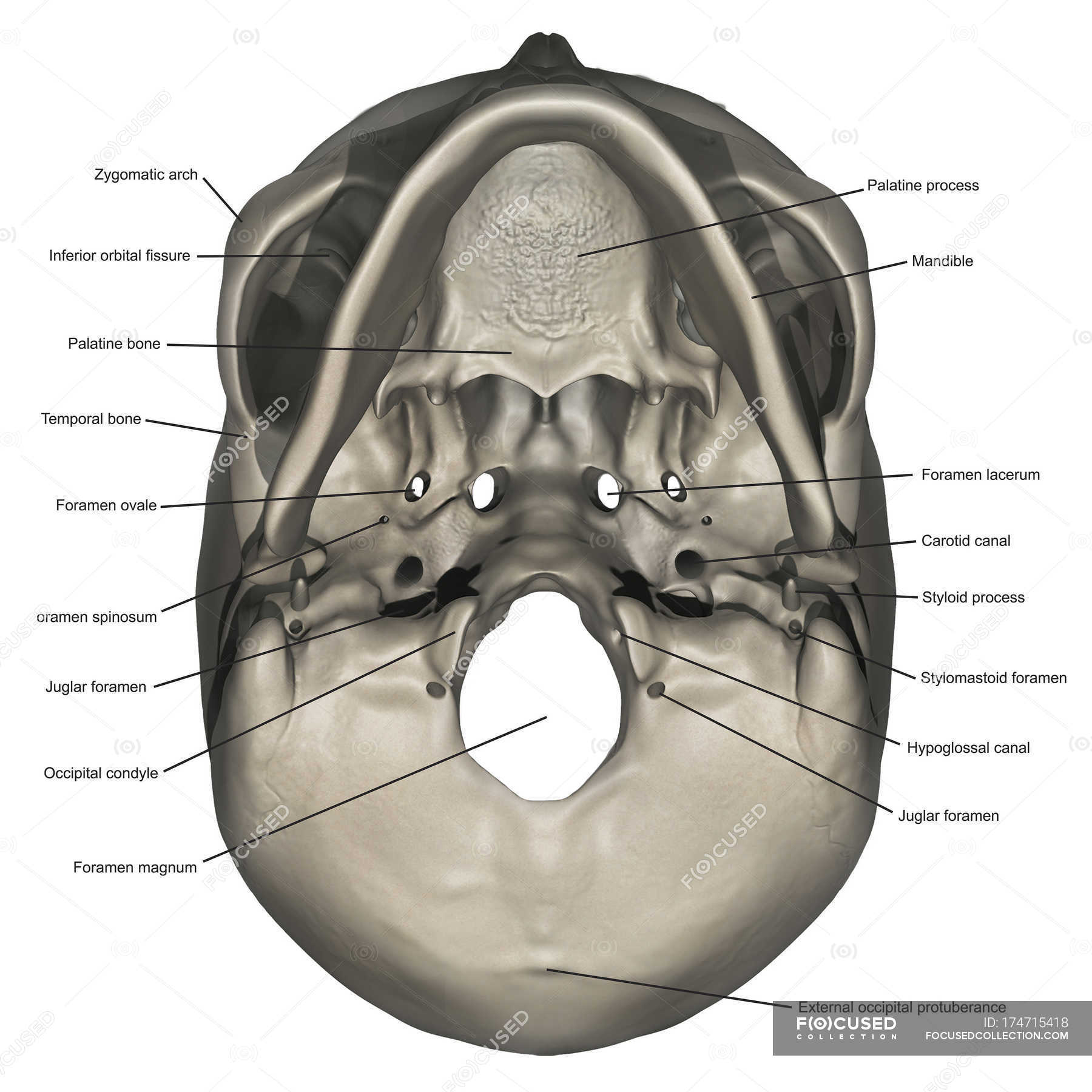
inferior skull & cranial cavity. this is the largest foramen of the skull; provides passage for the spinal cord to attach to the brain stem. foramen ovale (2, one right & one left) sphenoid bone. inferior skull & cranial cavity. these provide passage for branches of the paired (right and left) C.N. V trigeminal nerves. foramen spinosum (2, one.
Inferior view of the base of the skull Anatomy Kenhub
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/inferior-view-of-the-base-of-the-skull/Bw01R2EX0OMBLk18y7JCQ_inferior-base-of-the-skull_english.jpg)
Understand the protective role of the cranium for the brain and sensory organs. The Neurocranium Formed by the superior aspect of the skull, enclosing and protecting the brain, meninges an cerebral vasculature Anatomically separated into the Calvarium (roof) and base - Calvarium - Comprised of the frontal, occipital and two parietal bones - Base - Six bones, the frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid.
8.2.3 Markings of the Cranium Biology LibreTexts
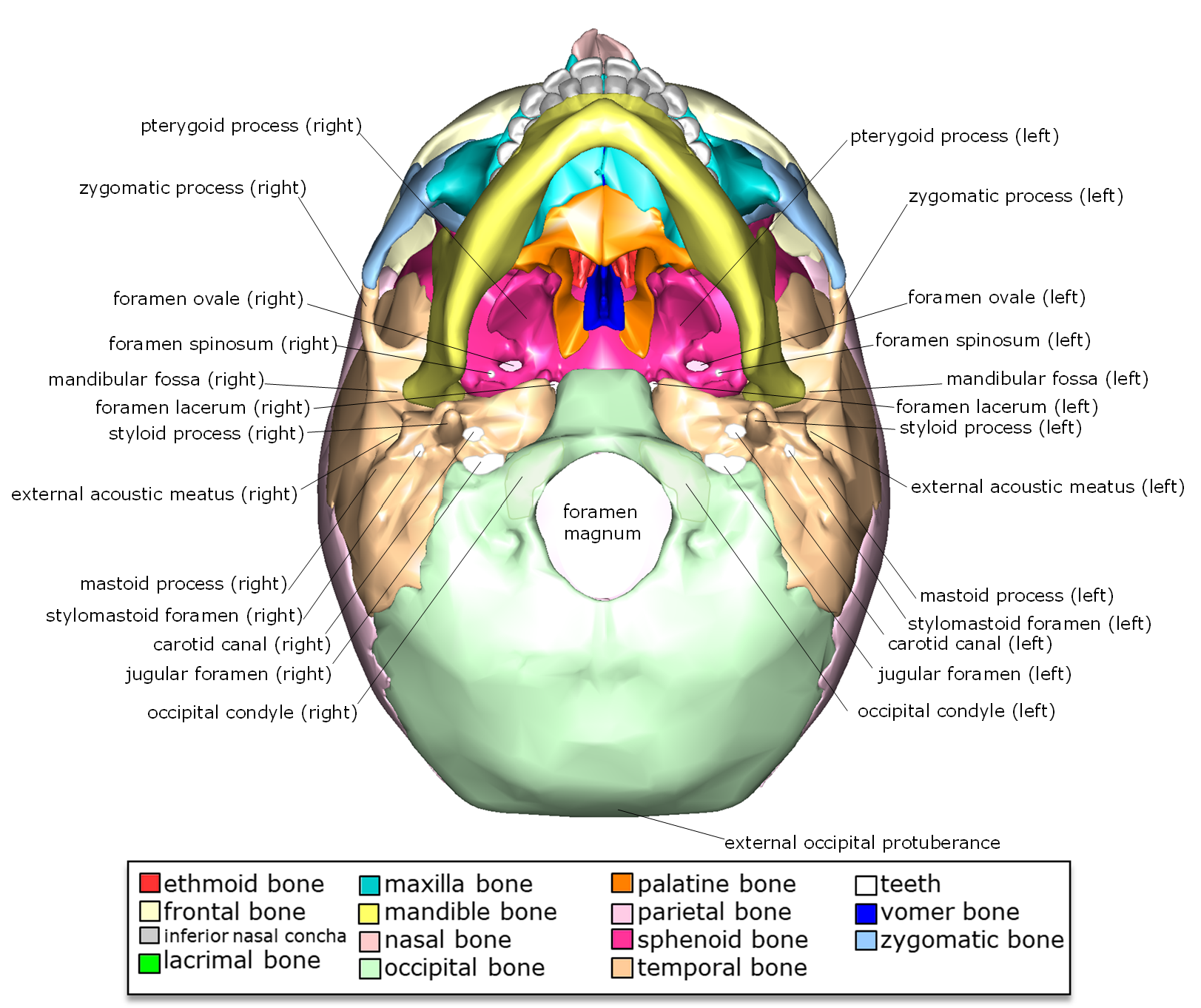
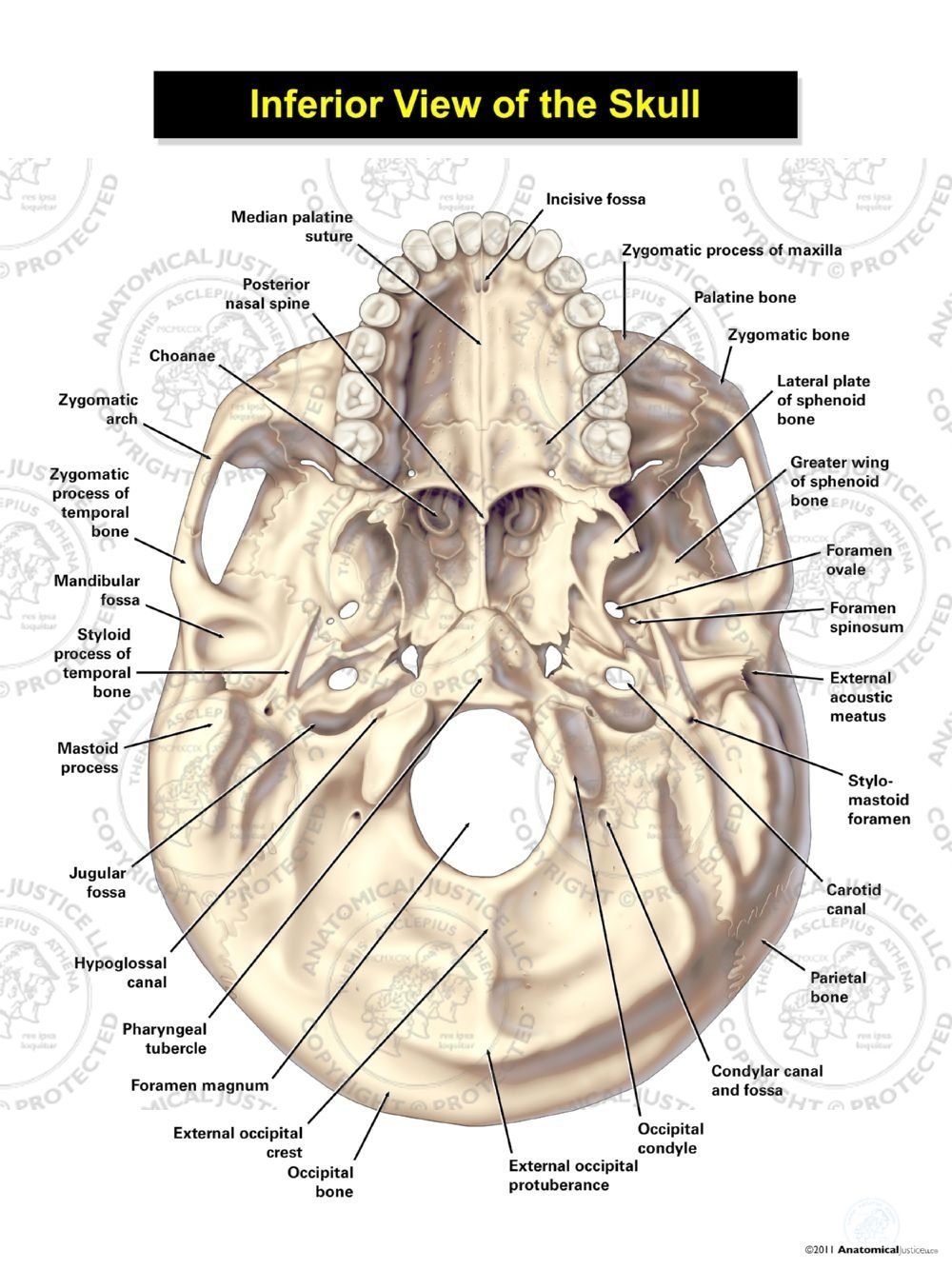
Inferior view of the base of the skull Author: Shahab Shahid MBBS • Reviewer: Dimitrios Mytilinaios MD, PhD Last reviewed: October 30, 2023 Reading time: 13 minutes Recommended video: Inferior view of the base of the skull [23:24] Structures seen on the inferior view of the base of the skull.
Inferior view of human skull anatomy with annotations — styloid process
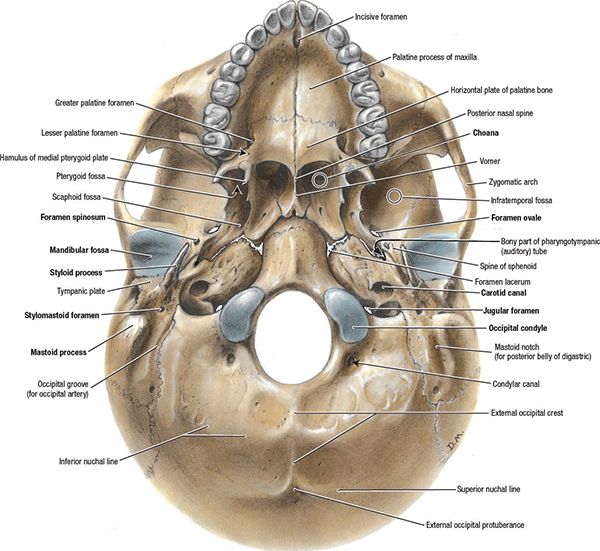
In an anterior view of the skull, the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone is easily seen inside the nasal opening as the upper nasal septum, but only a small portion of the vomer is seen as the inferior septum. A better view of the vomer bone is seen when looking into the posterior nasal cavity with an inferior view of the skull, where the.
Cranial Base Inferior View Anatomy wikitomy

A better view of the vomer bone is seen when looking into the posterior nasal cavity with an inferior view of the skull, where the vomer forms the full height of the nasal septum. The anterior nasal septum is formed by the septal cartilage , a flexible plate that fills in the gap between the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid and vomer bones.
Inferior view of the base of the skull Anatomy Kenhub
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/361/VamnYnBlLvYkS8hAb2S2FQ_inferior-base-of-the-skull-landmarks_english.jpg)
Interior of the Cranium. Above: Figure shows the view of the cranial cavity below. If the skull were sliced in the transverse plane (separating superior and inferior) to expose the inferior aspect of the cranial cavity, where the underside of the brain is supported by the skull, and it was viewed from above (superior view), the skull would appear as the two images below.
Interior View of the Inferior Skull

The facial bones of the skull form the upper and lower jaws, the nose, nasal cavity and nasal septum, and the orbit. The facial bones include 14 bones, with six paired bones and two unpaired bones. The paired bones are the maxilla, palatine, zygomatic, nasal, lacrimal, and inferior nasal conchae bones.
Inferior View of Skull
USMLE® Step 1 questions 0 / 2 complete Notes Figure 1: Anatomy of the cranial base, inferior view Figure 2: Anatomy of the hard palate and bony nasal septum, A. inferior view, and B. parasagittal view. Figure 3: Anatomy of the sphenoid bone, A. superior, B. inferior, and C. anterior views. Figure 4: Interior of the cranial base, superior view
Inferior View of the Skull
inferior view of the human skull. internal surface of the human skull. The internal surface of the human cranium. (more) In humans the base of the cranium is the occipital bone, which has a central opening (foramen magnum) to admit the spinal cord.
Inferior view of the base of the skull Anatomy Kenhub
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7567/Foramen_magnum.png)
Function The main function of the cranium is to protect the brain, which includes the cerebellum, cerebrum, and brain stem. It also gives a surface for the facial muscles to attach to.
Cranial Base Inferior View Anatomy pediagenosis
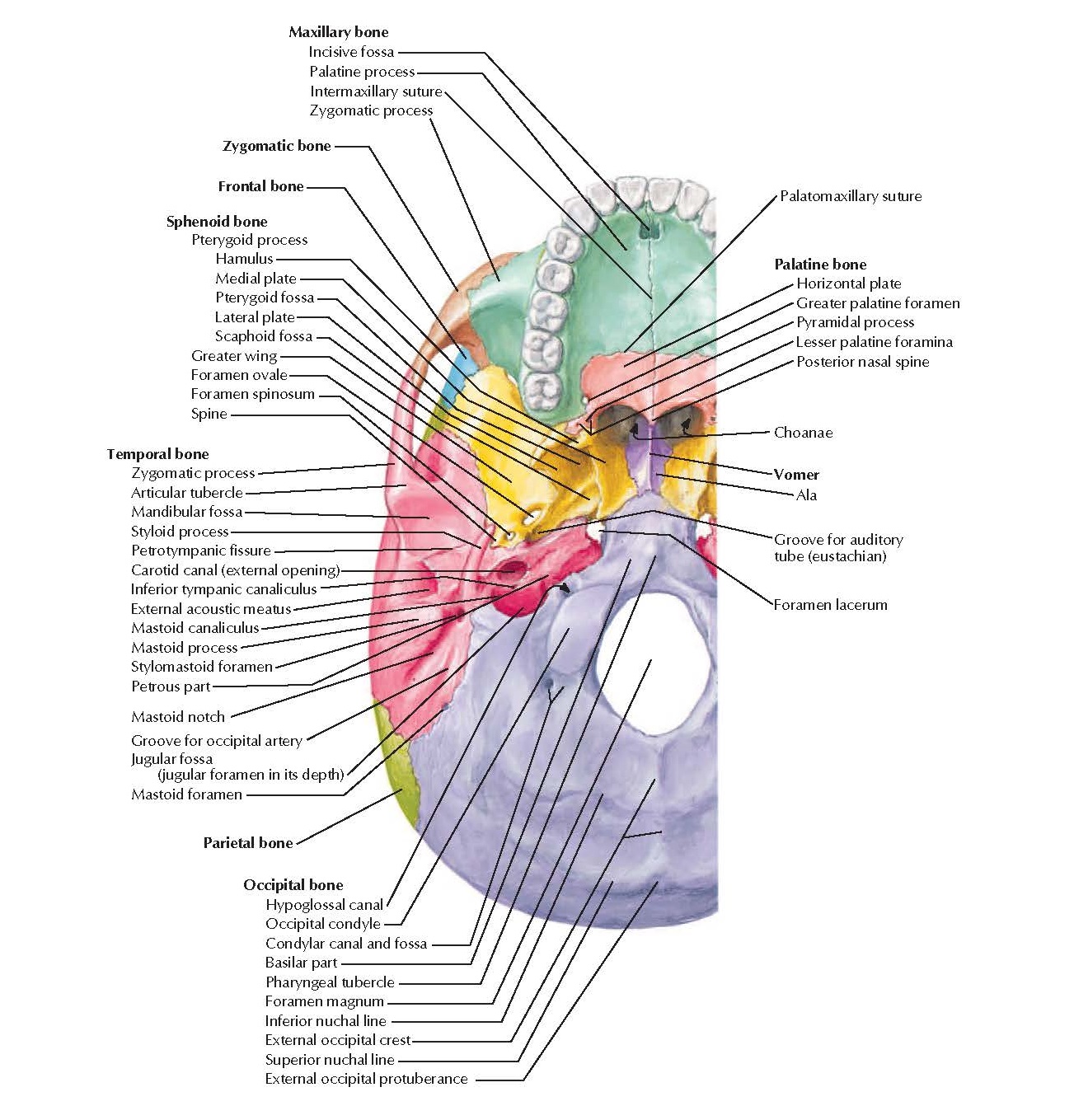
A, Inferior view of cranial base. The right pterygoid process has been sectioned and removed at its junction with the greater wing and body of the sphenoid bone to expose the pterygopalatine fossa and the vidian canal. The vidian nerve, formed by the union of the superficial and deep petrosal nerves, courses in the vidian canal, which passes.
Skull Definition, Anatomy, & Function Britannica

A short lecture by Dr. Kathleen Alsup introducing students to the anatomy of the skull from an inferior view.Check out our website (LINK BELOW) for additiona.