What is Refraction of light Leverage Edu

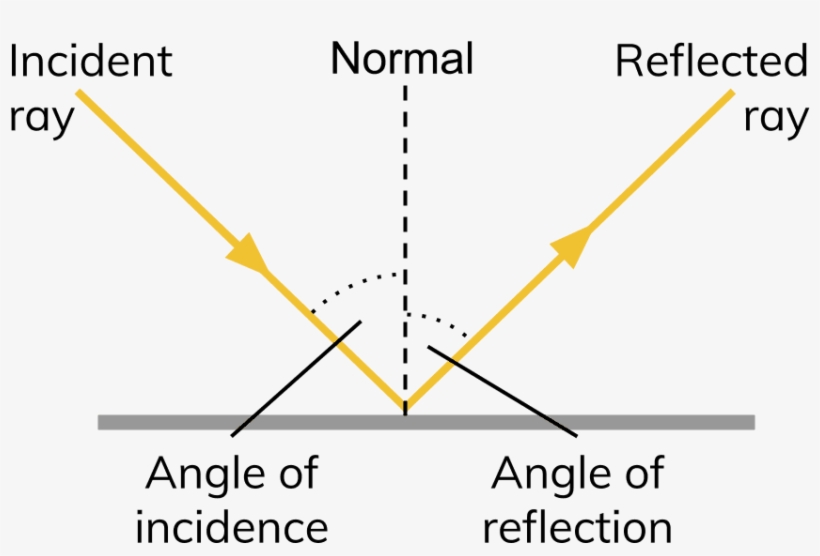
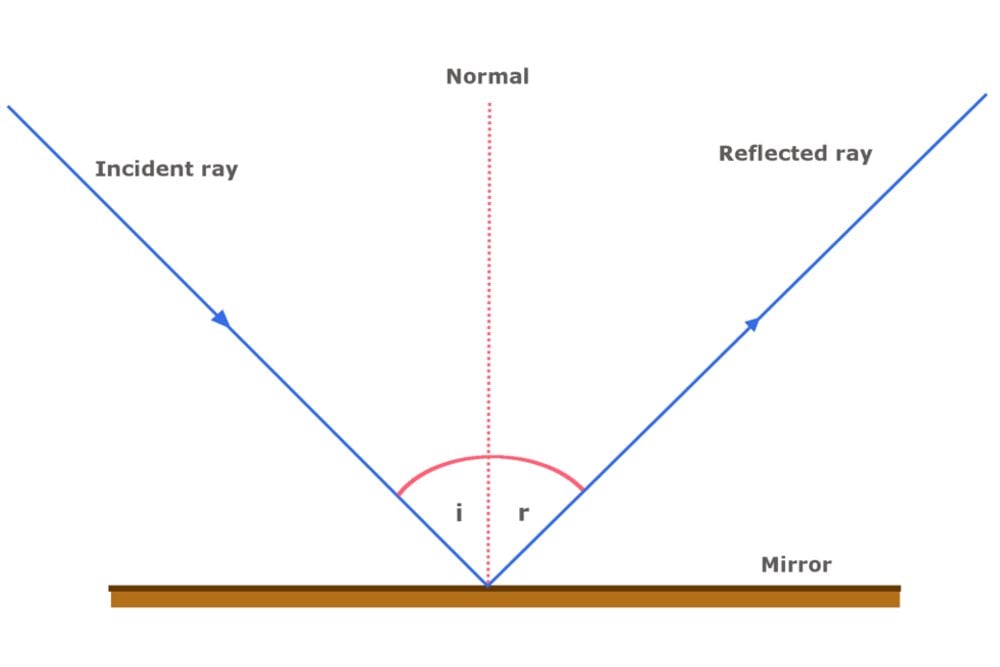
The angle the ray is reflected is always the same as the angle the light hits the mirror, with both angles being measured from the normal. This is summarised by the law of reflection, which states.
Angle of reflection equals angle of incidence polizuniversal

. The diagrams show a light ray being reflected at a plane mirror. The law of reflection states that: angle of incidence = angle of reflection For example, if a light ray hits a surface.
Diagram Of A Light Ray Being Reflected By Diagram Free Transparent PNG Download PNGkey
The reflection of light 7-25-00 Sections 23.1 - 23.3 Rays and wave fronts.. Consider an object placed a certain distance in front of a mirror, as shown in the diagram. To figure out where the image of this object is located, a ray diagram can be used. In a ray diagram, rays of light are drawn from the object to the mirror, along with the.
PPT CHAPTER 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION PowerPoint Presentation ID259858
Lesson 1: Reflection of light and Law of reflection. Law of reflection. Reflection. Science > UP Class 7th Science > Light > Reflection of light and Law of reflection. Let's draw a ray diagram to understand the path of light when it reflects off a mirror! Created by Vibhor Pandey. Questions Tips & Thanks. Want to join the conversation? Log.
Specular and diffuse reflection, vector illustration diagram VectorMine
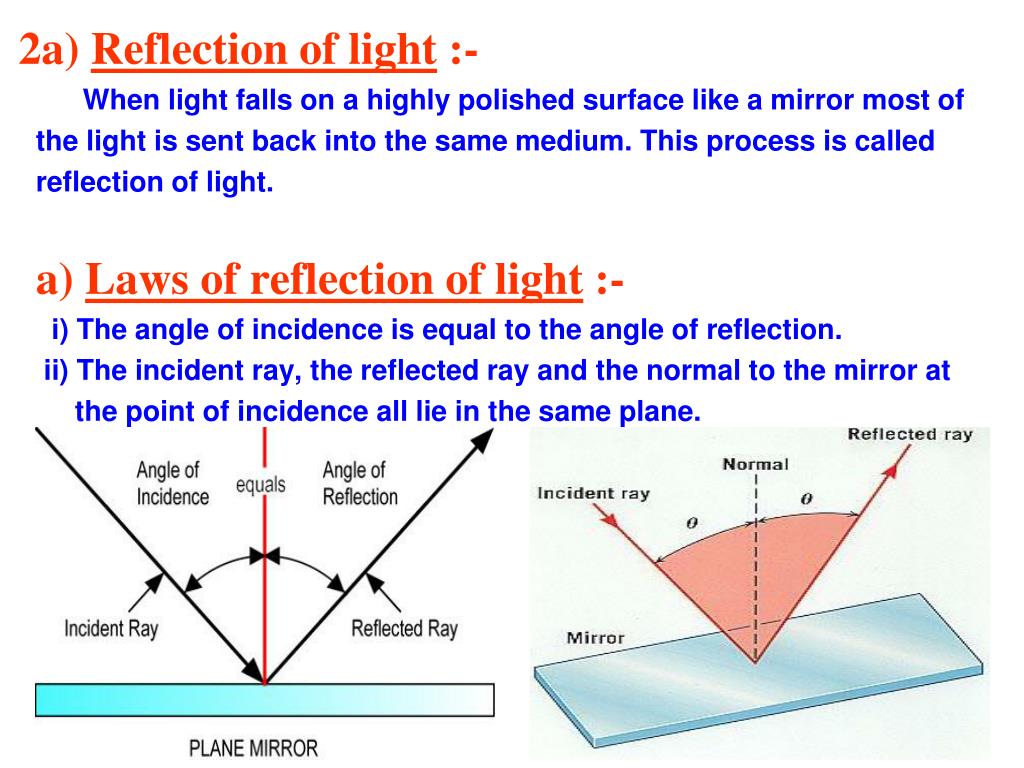
Definition: The Law of Reflection The angle at which a ray of light is incident on a surface is equal to the angle at which it is reflected, and on the opposite side of the normal. Mathematically, if the angle of incidence is 𝜃 and the angle of reflection is 𝜃 , then 𝜃 = 𝜃.
Reflection Of Light Leverage Edu

Example 3.6.1 3.6. 1. The diagram to the right shows the path of a ray of monochromatic light as it hits the surfaces between four different media (only the primary ray is considered - partial reflections are ignored). Order the four media according to the magnitudes of their indices of refraction. Solution.
Specular and Diffusion ReflectionHow Light Reflects MooMooMath and Science
The reflection of light is simplified when light is treated as a ray. This concept is illustrated in Figure 16.3, which also shows how the angles are measured relative to the line perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray strikes it. This perpendicular line is also called the normal line, or just the normal.
Reflection of Light Definition, Types, Laws & More Leverage Edu

1. Place a letter in the blank in order to classify the following objects as being either luminous (L) or illuminated (I) objects. Sun Moon Person Whiteboard Light bulb Candle 2. These diagrams are intended to represent the path of light from an object to an eye as the eye sights at the image of the object. Each diagram is incorrect.
Lab 10 Reflection and Refraction
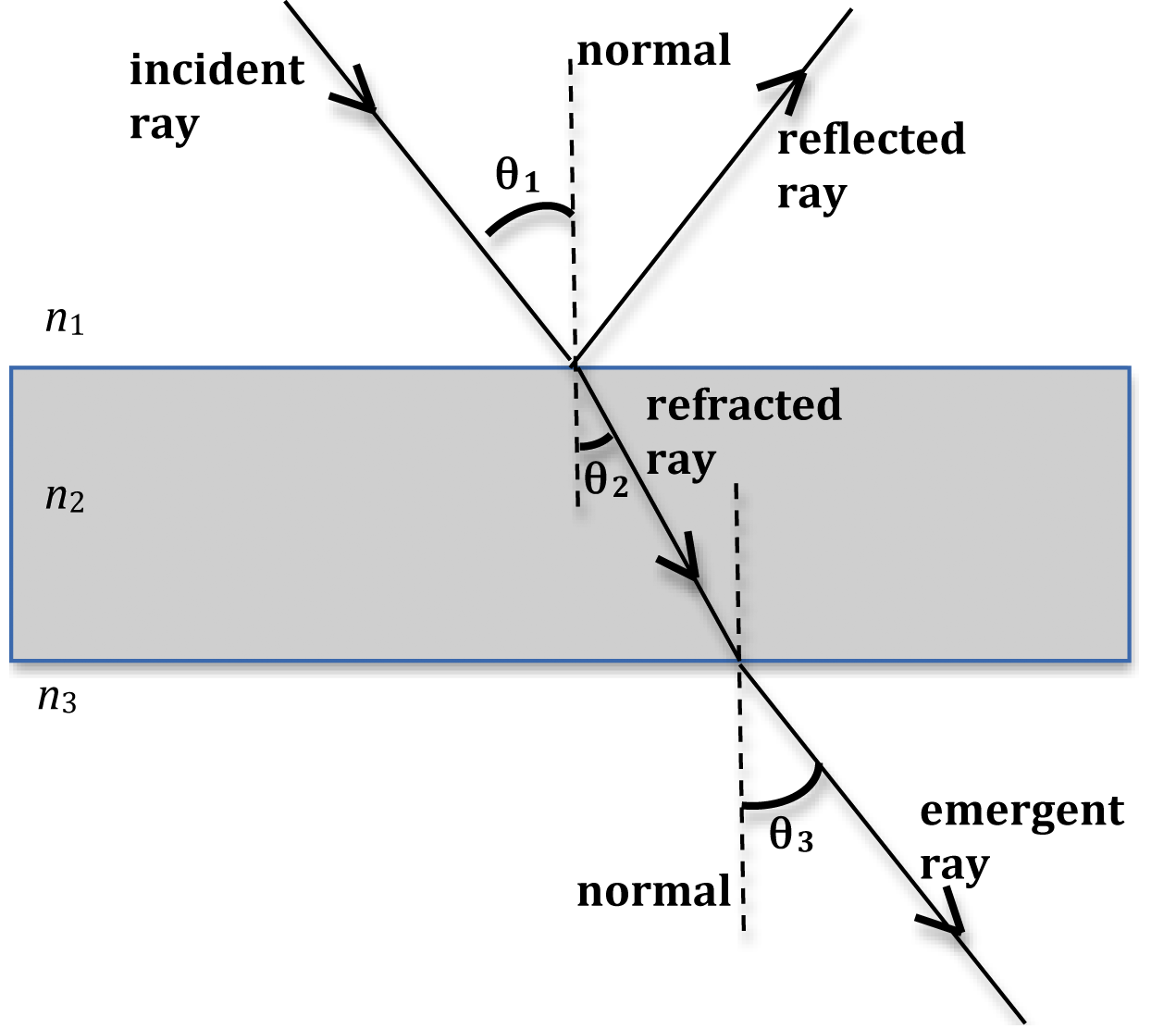
The angle of reflection is measured between a ray of light which has been reflected off a surface and an imaginary line called the normal. The normal. , the normal is an imaginary line drawn on a ray diagram perpendicular to, so at a right angle to (90 ), to the boundary between two media. If the boundary between the media is curved then the.
PPT Optics Reflection, Refraction & Total Internal Reflection PowerPoint Presentation ID3277716
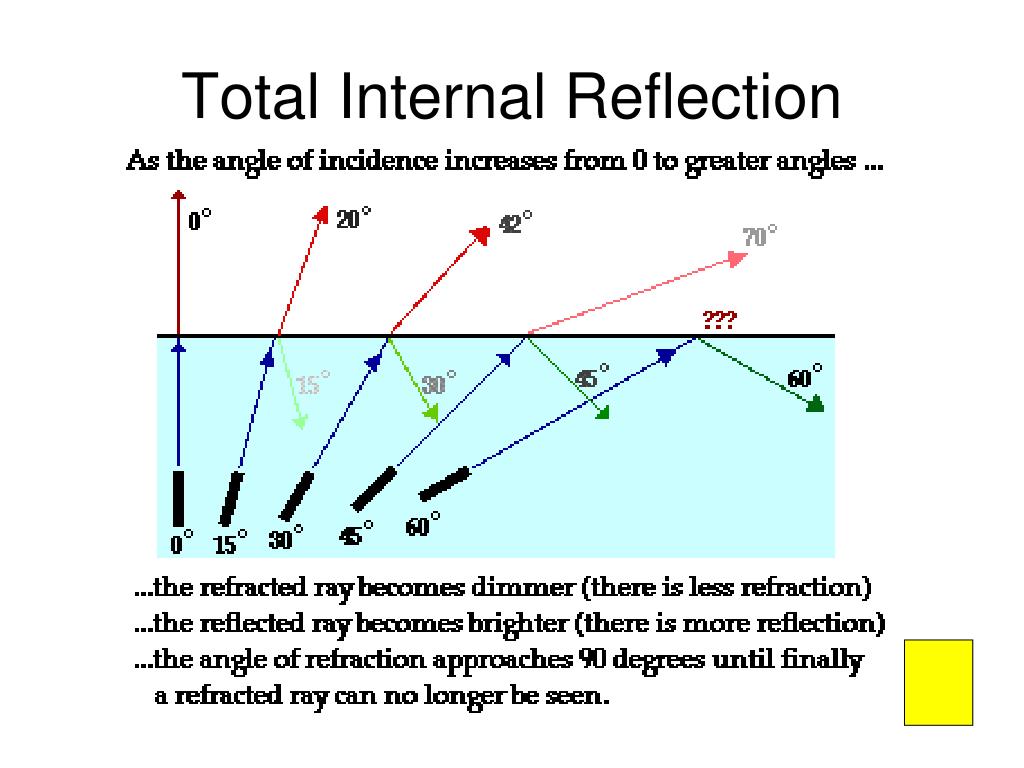
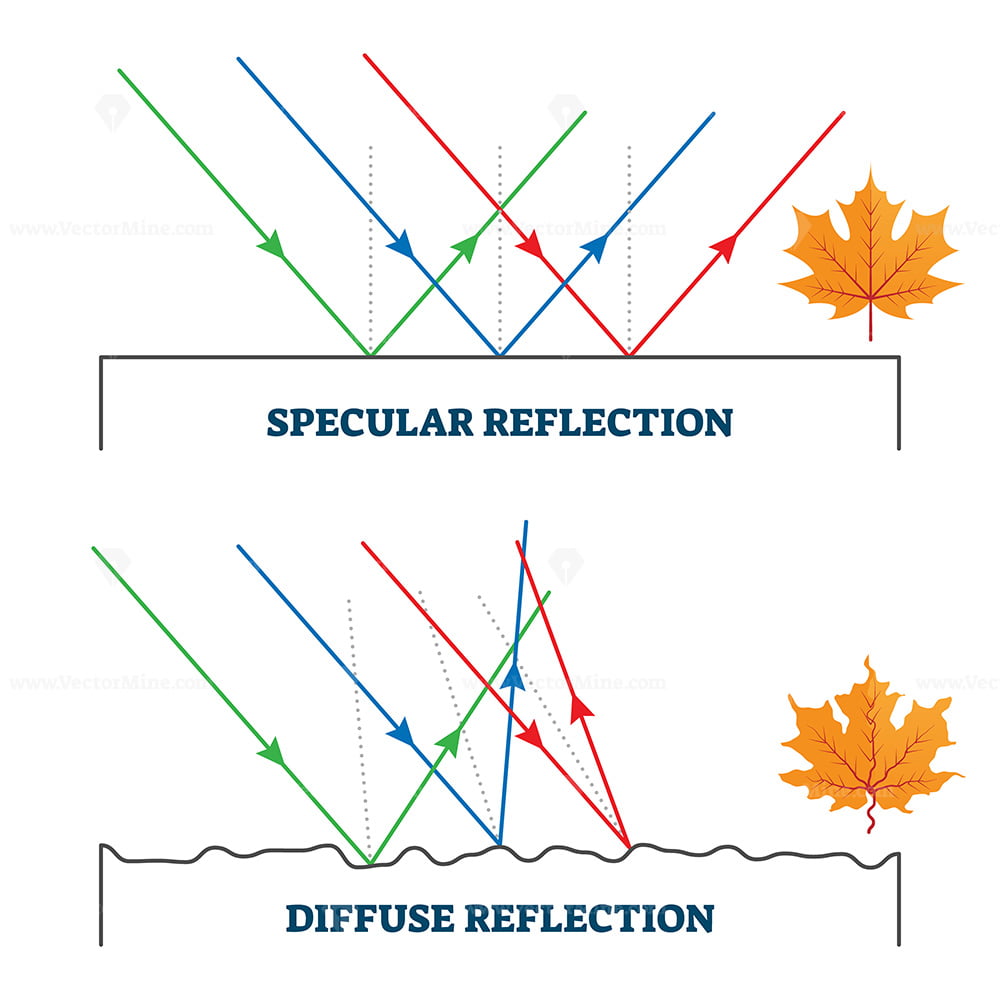
2,63,148 Types of Reflection of Light Different types of reflection of light are briefly discussed below: Regular reflection is also known as specular reflection Diffused reflection Multiple reflection Regular/ Specular Reflection Specular Reflection refers to a clear and sharp reflection, like the ones you get in a mirror.
Definition Diffuse Reflection Photokonnexion

A ray diagram shows how light travels, including what happens when it reaches a surface. In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: a straight line; with an arrowhead pointing in the direction.
Reflection of Light Definition, Types, Laws & More Leverage Edu

We use the diagram shown below to answer the questions. a) angle of incidence: i = 90 - 56 = 34 ° b)angle of reflection r = i = 34 ° (by the law of reflection) c) q = 90 - r = 90 - 34 = 56 ° d) i + r = 34 + 34 = 68 ° Example 2: A ray of light is reflected by two parallel mirrors (1) and (2) at points A and B.
Reflection, Refraction and Diffraction The Science and Maths Zone

When a ray of light falls on any object (polished, smooth, shiny object), light from that object bounces back those rays of light to our eyes and this is known as "Reflection" or "Reflection of Light". This phenomenon is what enables us to look at the world around us based. Before, after and during reflection light travels in a straight line.
CHAPTER 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION(CBSE CLASS 10) DEX ACADEMY
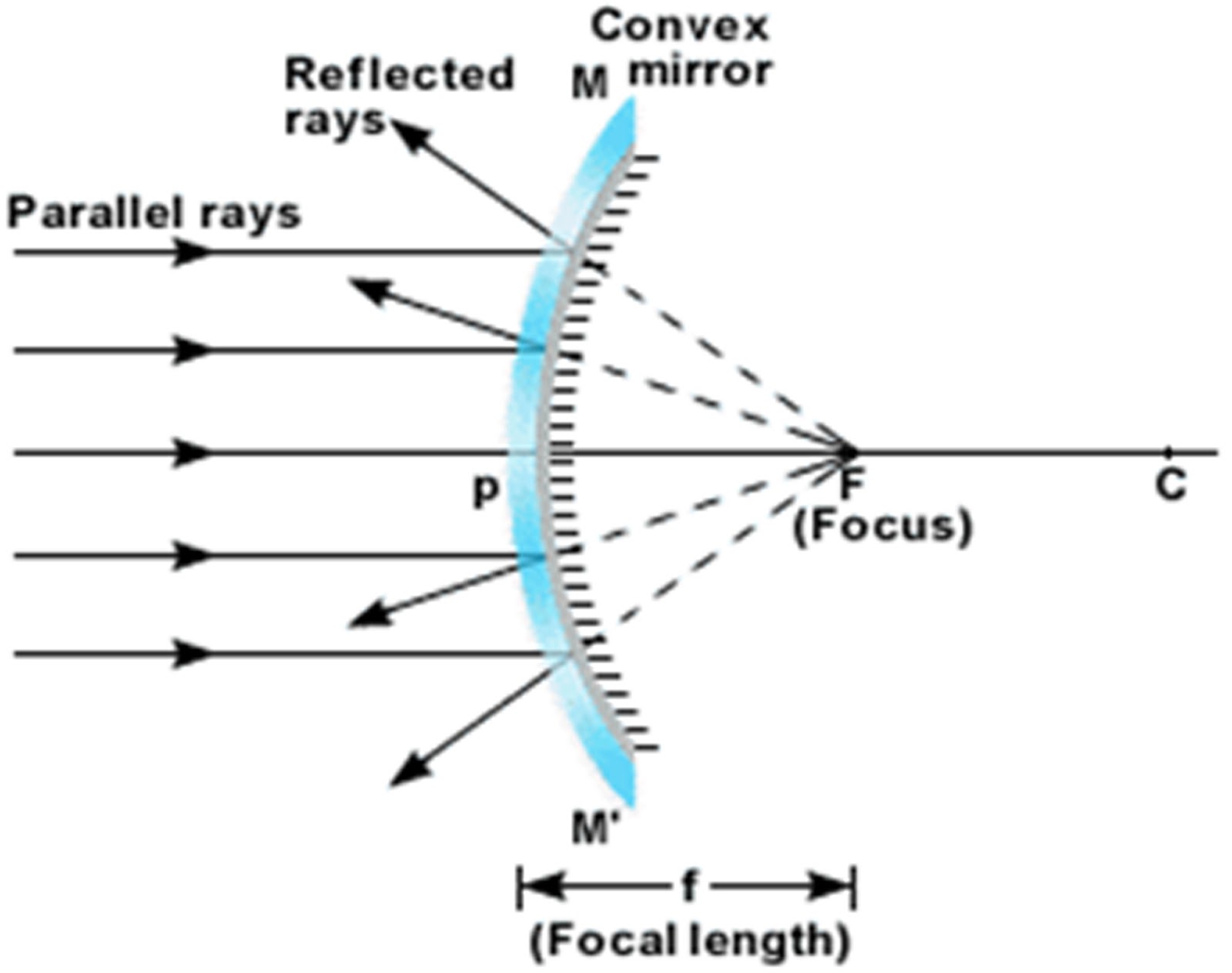
The law of reflection is illustrated in Figure 1.3.1 1.3. 1, which also shows how the angle of incidence and angle of reflection are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray strikes. Figure 1.3.1 1.3. 1: The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence—θ r.
Reflection of Light Class 8, Light
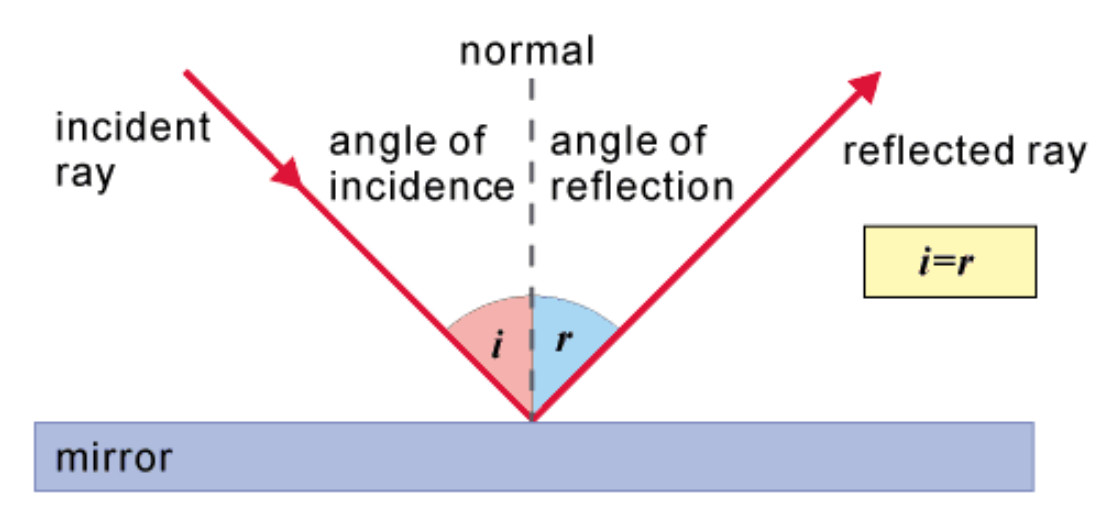
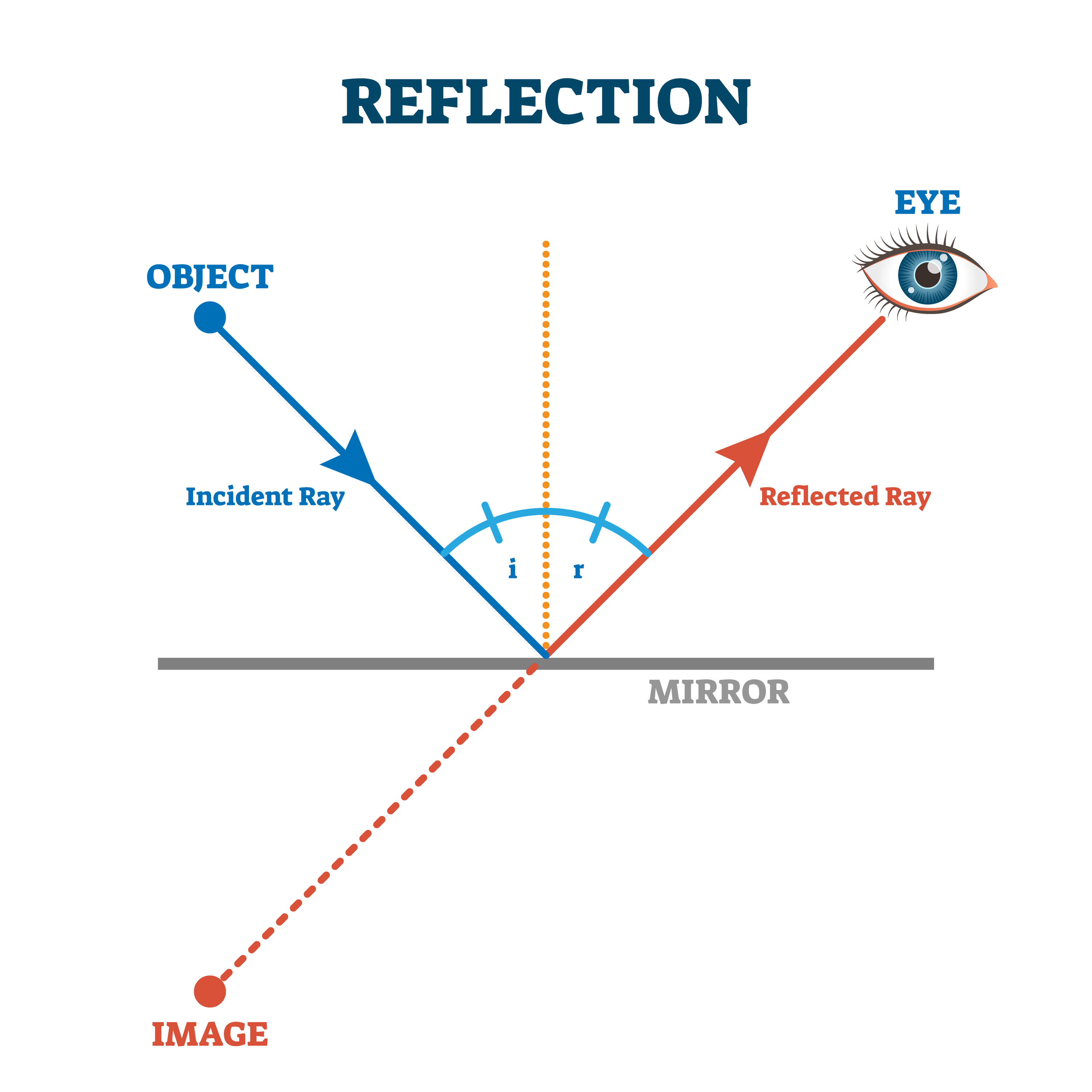
The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The ray of light that leaves the mirror is known as the reflected ray (labeled R in the diagram).
What Is The Law Of Reflection Definition And A Simple Explanation
Reflection is when light bounces off an object. If the surface is smooth and shiny, like glass, water or polished metal, the light will reflect at the same angle as it hit the surface. This is called specular reflection. Diffuse reflection is when light hits an object and reflects in lots of different directions. This happens when the surface.