
Types of Special Motor Classification of Electric Motor Types of

Electrical motors can be brushed or brushless, Electrical motors can be single-phase or three phase. Electrical motors could be air-cooled or liquid-cooled. Electrical motors can be powered by direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC). Standard electrical motors can be found all around you, think of an electric fan, a pump, household.
TYPES OF AN ELECTRIC MOTORS Engineering Feed

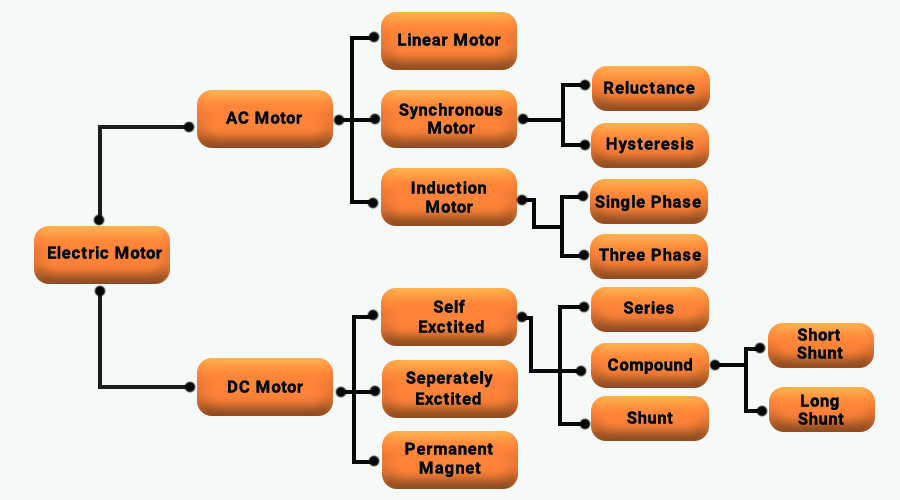
Types of Electric Motors. The various types of motors include: DC Motors. Synchronous Motors. 3 Phase Induction Motors (a type of induction motor) Single Phase Induction Motors (a type of induction motor) Other special, hyper-specific motors. The motors have been classified in the diagram below: Among the four basic classifications of motors.
Types of Electric Motors and Their Use Linquip

The design of electric motors used today is more complex than what will be discussed in this lesson, but the general principles are the same for all types of motors. An electric motor is a product.
Leisure, Travel and Tourism with Loveu Electric Motors Types

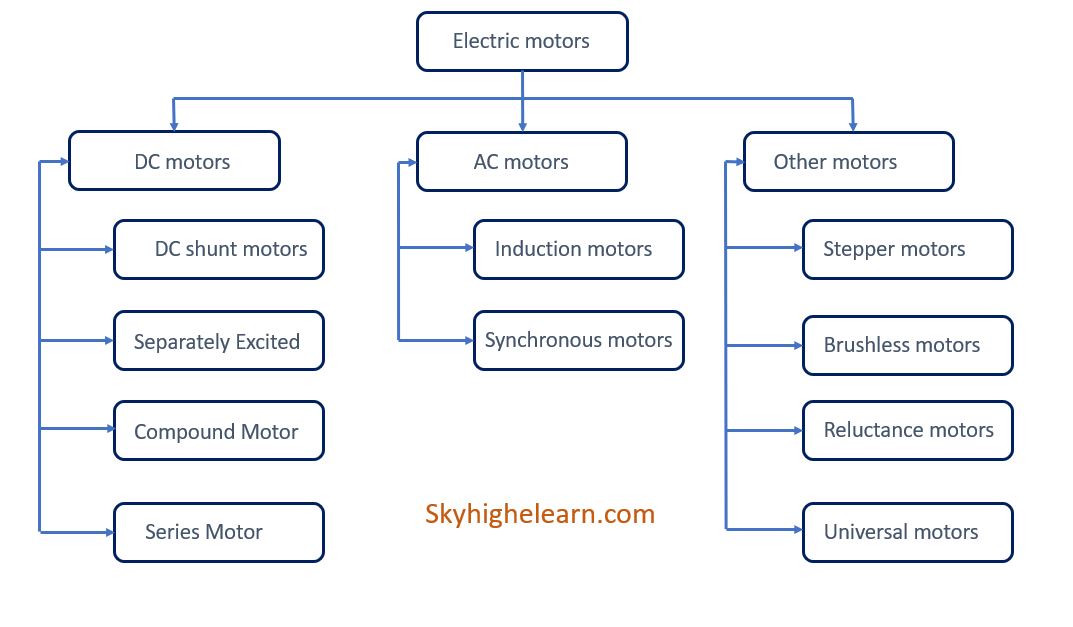
Following are the types of electric motors which are described below: DC Motor Shunt motor Separately excited motor Series motor Compound motor PMDC motor AC Motor Induction motor 1-phase induction motor 3-phase induction motor Synchronous motor Stepper motor Brushless motor Universal motor Hysteresis motor Reluctance motor Linear Motor
What Is An Electric Motor?

Both rotary and linear actuators are used. Low-cost brushed DC motors are common, but are being superseded by brushless AC motors for high-performance applications. Stepper Motors Stepper motors use an internal rotor, electronically manipulated by external magnets. The rotor can be made with permanent magnets or a soft metal.
Types of Electric Motor and Uses AC and DC Motor Explained Details
Types of Electric Motors. With two basic types, electric motors can be broadly classified into various types, as illustrated in the diagram. AC Electric Motors. AC motors provide mechanical energy from electrical input and are common electric motors that drive an alternating current. These motors are extensively used in a wide variety of.
Types of Electric Motors Their Working & Applications [PDF]

Explained with functions and applications- Electric motor, Stepper motor, Servo motor, Linear motor, Hydraulic motor, Pneumatic motor, Brushless DC motor, Universal motor, Traction motor, Gear motor, Hollow shaft motor, and Internal combustion engines. Skip to content DipsLab.com by Dipali Chaudhari Menu PLC MATLAB Electrical GATE
Types of Electric Motors Classification of Electric Motors, AC Motor

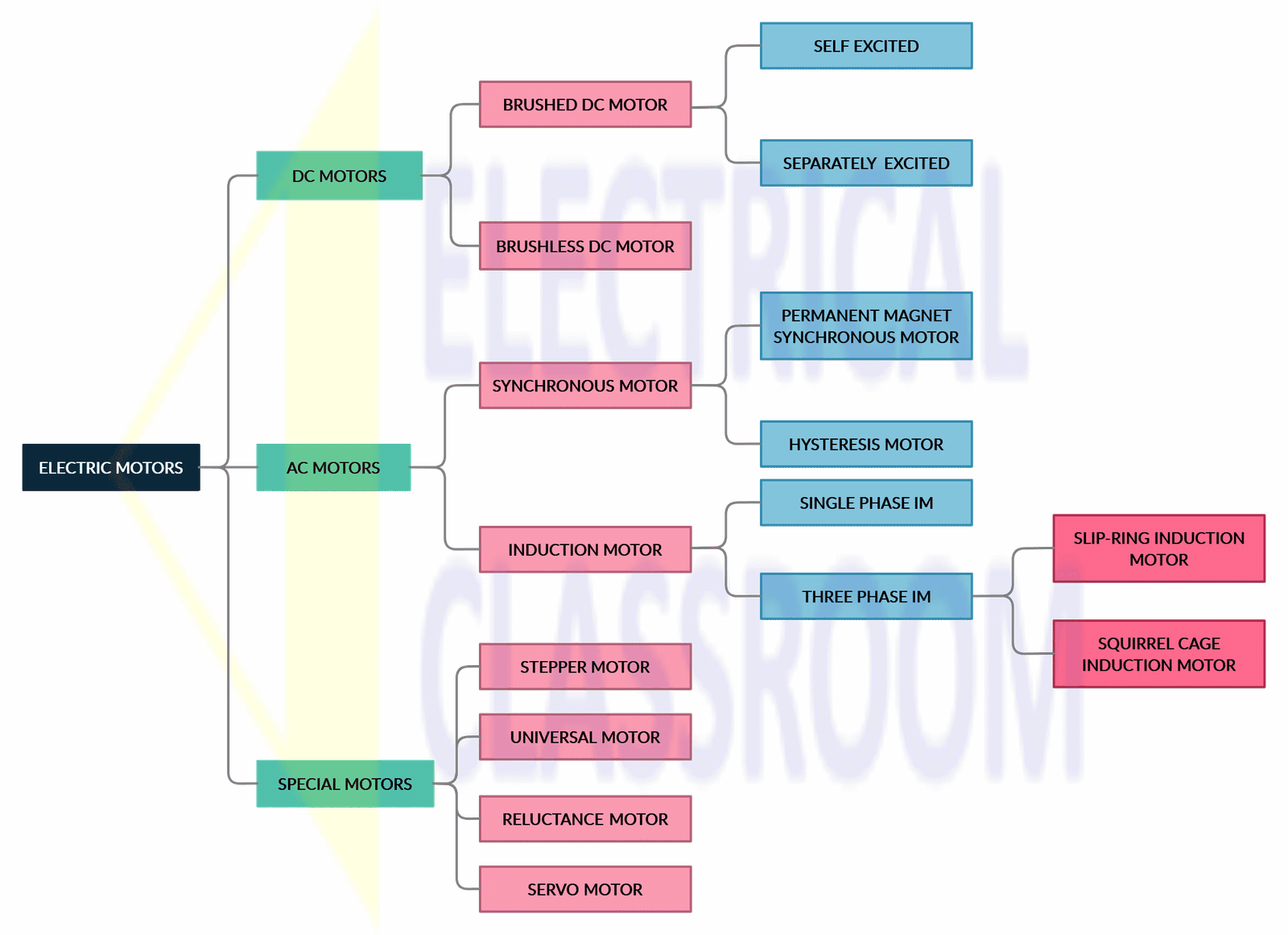
This article discusses the distinctions between DC motors and other types of electric motors, including the various types of DC motors and their respective functionalities and control mechanisms. DC motors are powered by direct current. What distinguishes a DC motor from other types of electric motors. DC motor type 1 - brushed DC motor.
Different Types of Electric Motors and Their Applications

The direct current electric motor can be, in turn, a permanent induction motor or a direct induction motor. In addition to these more general classifications, there are also other more modern types of motors, such as stepper motors and linear motors. Alternating current electric motors. AC motor can be classified as universal motor, synchronous.
What are the Different Types of Electric Motors?

Types of Electric Motors AC Motors 1.) Synchronous Motor 2.) Asynchronous Motor or Induction Motor DC Motors 1). Separately Excited DC Motor 2). DC Series Motor 3). Shunt DC Motor 4.) Compound DC Motor 5). PMDC Motor Special Purpose Motors 1). Brushless DC Motors 2). Stepper Motor 3). Universal Motor
Electrical and Electronics Engineering Types of Electric Motors
linear motor commutator rotor stator electric motor, any of a class of devices that convert electrical energy to mechanical energy, usually by employing electromagnetic phenomena. Most electric motors develop their mechanical torque by the interaction of conductors carrying current in a direction at right angles to a magnetic field.
What is an Electric Motor?
The two main types of electric motors are AC and DC motors. These are the main types because the type of current which is supplied to the electric motor determines how it will operate, as well as its optimal design and other factors. AC electric motor depends on an alternating current supply to operate, while DC motor uses direct current.
How an electric motor works in a car Electric Motor Engineering
Rotor, Commutator and Brushes Putting It All Together How an AC Motor Works AC Rotor and Stator Motors Everywhere! Inside an Electric Motor You might be surprised to find out just how much work is done by electric motors. HowStuffWorks To understand how an electric motor works, the key is to understand how the electromagnet works.
Types of electric motors and their applications
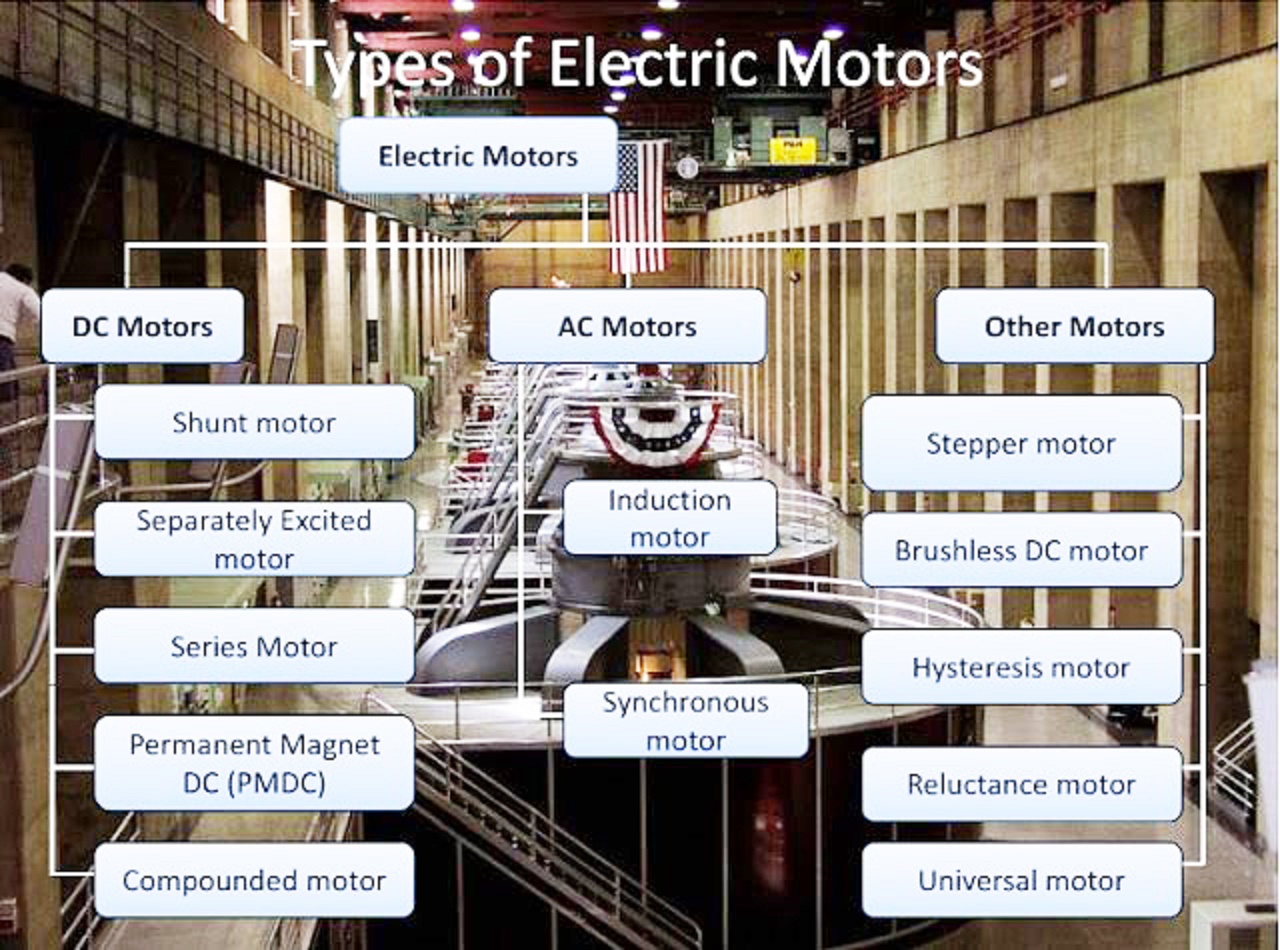
Motor Classification. An electric motor is a device which converts electrical energy into kinetic energy (i.e. motion). Most motors described in this guide spin on an axis, but there are also specialty motors that move linearly. All motors are either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC), but a few can operate on both (See Figure 2-1).
Different Types of Motors 3dprintinginfographic Electronic

An electrical motor is mainly classified into three types. AC Motors DC Motors Special Motors Table of Contents AC Motor Synchronous Motor Excited Synchronous Motor Single Phase Synchronous Motor Three Phase Synchronous Motor Unexcited Synchronous Motor Reluctance Motor Hysteresis Motor Asynchronous Motor Induction Motor
Types of Motors. Electricity, Electric motor, Electrical circuit diagram

An electric motor is a device used to convert electricity into mechanical energy—opposite to an electric generator.They operate using principles of electromagnetism, which shows that a force is applied when an electric current is present in a magnetic field.This force creates a torque on a loop of wire present in the magnetic field, which causes the motor to spin and perform useful work.